| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2021-09-14 15:41:38 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000939 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | S-Adenosylhomocysteine |
|---|
| Description | S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine (SAH) is formed by the demethylation of S-adenosyl-L-methionine. S-Adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy or SAH) is also the immediate precursor of all of the homocysteine produced in the body. The reaction is catalyzed by S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and is reversible with the equilibrium favoring formation of SAH. In vivo, the reaction is driven in the direction of homocysteine formation by the action of the enzyme adenosine deaminase which converts the second product of the S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase reaction, adenosine, to inosine. Except for methyl transfer from betaine and from methylcobalamin in the methionine synthase reaction, SAH is the product of all methylation reactions that involve S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as the methyl donor. Methylation is significant in epigenetic regulation of protein expression via DNA and histone methylation. The inhibition of these SAM-mediated processes by SAH is a proven mechanism for metabolic alteration. Because the conversion of SAH to homocysteine is reversible, with the equilibrium favoring the formation of SAH, increases in plasma homocysteine are accompanied by an elevation of SAH in most cases. Disturbances in the transmethylation pathway indicated by abnormal SAH, SAM, or their ratio have been reported in many neurodegenerative diseases, such as dementia, depression, and Parkinson's disease (PMID:18065573 , 17892439 ). Therefore, when present in sufficiently high levels, S-adenosylhomocysteine can act as an immunotoxin and a metabotoxin. An immunotoxin disrupts, limits the function, or destroys immune cells. A metabotoxin is an endogenous metabolite that causes adverse health effects at chronically high levels. Chronically high levels of S-adenosylhomocysteine are associated with S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) hydrolase deficiency and adenosine deaminase deficiency. S-Adenosylhomocysteine forms when there are elevated levels of homocysteine and adenosine. S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine is a potent inhibitor of S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent methylation reactions. It is toxic to immature lymphocytes and can lead to immunosuppression (PMID:221926 ). |
|---|
| Structure | N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N)C(O)=O InChI=1S/C14H20N6O5S/c15-6(14(23)24)1-2-26-3-7-9(21)10(22)13(25-7)20-5-19-8-11(16)17-4-18-12(8)20/h4-7,9-10,13,21-22H,1-3,15H2,(H,23,24)(H2,16,17,18)/t6-,7+,9+,10+,13+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (2S)-2-Amino-4-({[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl]methyl}sulfanyl)butanoic acid | ChEBI | | 2-S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine | ChEBI | | Adenosyl-L-homocysteine | ChEBI | | Adenosylhomocysteine | ChEBI | | AdoHcy | ChEBI | | S-(5'-Adenosyl)-L-homocysteine | ChEBI | | S-[1-(Adenin-9-yl)-1,5-dideoxy-beta-D-ribofuranos-5-yl]-L-homocysteine | ChEBI | | SAH | ChEBI | | (2S)-2-Amino-4-({[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl]methyl}sulfanyl)butanoate | Generator | | (2S)-2-Amino-4-({[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl]methyl}sulphanyl)butanoate | Generator | | (2S)-2-Amino-4-({[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxytetrahydrofuran-2-yl]methyl}sulphanyl)butanoic acid | Generator | | S-[1-(Adenin-9-yl)-1,5-dideoxy-b-D-ribofuranos-5-yl]-L-homocysteine | Generator | | S-[1-(Adenin-9-yl)-1,5-dideoxy-β-D-ribofuranos-5-yl]-L-homocysteine | Generator | | (S)-5'-(S)-(3-Amino-3-carboxypropyl)-5'-thioadenosine | HMDB | | 5'-Deoxy-S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine | HMDB | | 5'-S-(3-Amino-3-carboxypropyl)-5'-thio-L-adenosine | HMDB | | Adenosyl-homo-cys | HMDB | | Adenosylhomo-cys | HMDB | | Formycinylhomocysteine | HMDB | | L-5'-S-(3-Amino-3-carboxypropyl)-5'-thior-adenosine | HMDB | | L-S-Adenosyl-homocysteine | HMDB | | L-S-Adenosylhomocysteine | HMDB | | S-(5'-Deoxyadenosin-5'-yl)-L-homocysteine | HMDB | | S-(5'-Deoxyadenosine-5')-L-homocysteine | HMDB | | S-Adenosyl-homocysteine | HMDB | | S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine | HMDB | | Adenosylhomocysteine, S | HMDB | | S Adenosylhomocysteine | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C14H20N6O5S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 384.411 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 384.12158847 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2S)-2-amino-4-({[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl}sulfanyl)butanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 979-92-0 |
|---|
| SMILES | N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C14H20N6O5S/c15-6(14(23)24)1-2-26-3-7-9(21)10(22)13(25-7)20-5-19-8-11(16)17-4-18-12(8)20/h4-7,9-10,13,21-22H,1-3,15H2,(H,23,24)(H2,16,17,18)/t6-,7+,9+,10+,13+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | ZJUKTBDSGOFHSH-WFMPWKQPSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as gamma butyrolactones. Gamma butyrolactones are compounds containing a gamma butyrolactone moiety, which consists of an aliphatic five-member ring with four carbon atoms, one oxygen atom, and bears a ketone group on the carbon adjacent to the oxygen atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Lactones |
|---|
| Sub Class | Gamma butyrolactones |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Gamma butyrolactones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Gamma butyrolactone
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- 1,2-diol
- Oxacycle
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
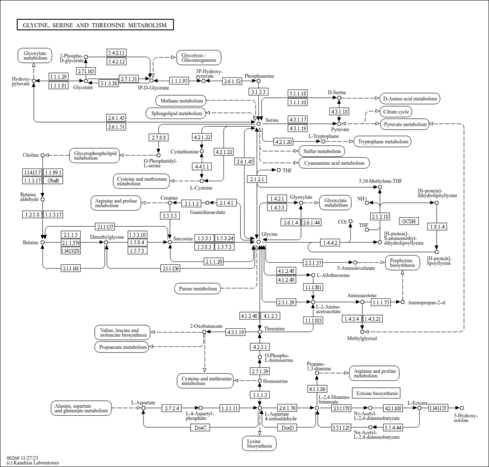
| Process | Naturally occurring processBiological processBiochemical pathwayMetabolic pathway- Glycine and Serine Metabolism (HMDB: HMDB0000939)
- Carnitine Synthesis (HMDB: HMDB0000939)
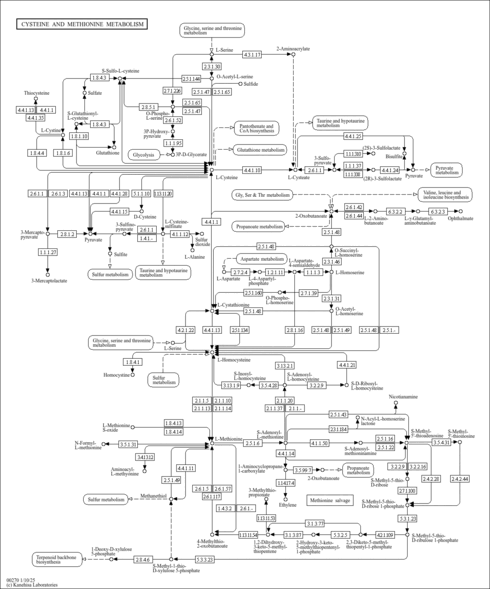
- Methionine Metabolism (HMDB: HMDB0000939)
- Betaine Metabolism (HMDB: HMDB0000939)
- Porphyrin Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0000953)
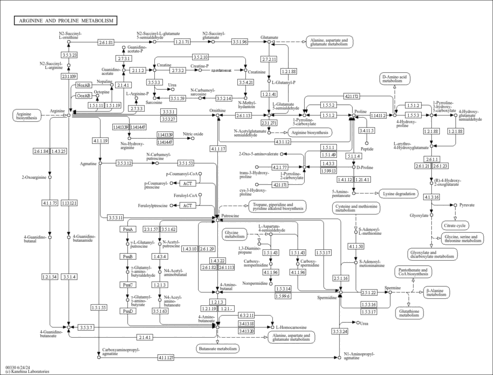
- Arginine and Proline Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0012004)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0014212)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014219)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014221)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014250)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014258)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014278)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014280)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014307)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014316)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014338)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014366)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014367)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0063808)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063822)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063831)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063834)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063835)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0063836)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063844)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0063846)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063849)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063866)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063867)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0063870)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063884)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063888)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069980)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069983)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069986)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069987)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069996)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070008)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0070011)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070015)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070018)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070022)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070023)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070024)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070043)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070046)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070058)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070065)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070072)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070073)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070078)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070088)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070089)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070090)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070102)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070110)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070123)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070132)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070133)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070136)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070139)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070140)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070143)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070146)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070148)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070150)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070153)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070157)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070160)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070170)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070175)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070178)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070192)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070196)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070204)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070207)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070214)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070217)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070225)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070235)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070237)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070239)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070243)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070244)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070253)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070255)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070256)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070266)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070270)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070285)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070286)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070292)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070294)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070299)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070300)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070311)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070312)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070314)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070316)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070317)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070318)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070319)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070336)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070337)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070339)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070340)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070343)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070347)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070350)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070355)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070358)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070360)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070365)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070366)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070381)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070382)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070384)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070389)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070390)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070392)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070396)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070397)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070398)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070399)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070402)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070406)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070409)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080467)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070411)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070412)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070415)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080443)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080446)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080449)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080450)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080451)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080452)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080453)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080457)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080469)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080479)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080485)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0080490)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080493)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080498)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080511)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080525)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080528)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080529)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080530)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080533)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080549)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080552)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080554)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080562)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080563)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080568)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080573)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080577)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080579)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080585)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080589)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080592)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080595)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080599)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080609)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080615)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080616)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080627)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080632)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080634)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080636)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080639)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080643)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080645)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080657)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080659)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080667)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080668)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080672)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080674)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080690)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080695)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080697)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080699)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080706)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080713)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080716)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080721)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080723)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080726)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080727)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080729)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080731)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080737)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080745)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080750)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080751)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080752)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080755)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080756)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080758)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080771)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080775)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080776)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080777)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080780)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080782)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080783)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080790)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080799)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080820)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080821)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080826)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080833)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086835)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080834)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080843)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080849)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080853)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080854)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080866)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086740)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086742)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0086743)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086745)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086756)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086765)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086767)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086777)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086782)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0086798)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086800)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086803)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086805)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086823)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086828)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086836)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086847)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086854)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086858)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086882)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0086918)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086922)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086934)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086941)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086946)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086948)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086963)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0086966)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086967)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0086979)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086995)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087002)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087015)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087020)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087022)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087024)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0087025)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087030)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087032)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087052)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087066)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087083)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087107)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087110)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087115)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087118)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087123)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0087124)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087125)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087129)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087131)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087135)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087137)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087144)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087148)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087170)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087188)
- Ubiquinone Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0087215)
- Histidine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087314)
- Tyrosine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087328)
- Secondary Metabolites: Ubiquinol Biosynthesis 2 (PathBank: SMP0122225)
- Biotin Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0000785)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014222)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014249)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014277)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014308)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014309)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014337)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014339)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014344)
- Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063643)
- Tryptophan Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063693)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063820)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063842)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063875)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063880)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069989)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069994)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070004)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070006)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070009)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0070010)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070047)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070054)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070084)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070111)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070127)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070135)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070149)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070159)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070171)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070212)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070215)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070223)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070240)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070248)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070252)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070277)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070280)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070282)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070298)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070309)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070313)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070324)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070338)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070341)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070371)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070400)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070413)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0080430)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080448)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080477)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080483)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080484)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080486)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0080487)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080500)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080506)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080508)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080523)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080546)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080547)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080561)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080590)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080600)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080604)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080606)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080611)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080620)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080637)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080638)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080641)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080642)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080648)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080649)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080651)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080661)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080670)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080677)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080680)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080681)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080698)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080710)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080738)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080743)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080754)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080769)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080796)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080800)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080804)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080807)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080817)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080825)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080842)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080857)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0086733)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086776)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0086779)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086795)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086802)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0086806)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086840)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086845)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086856)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086860)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086863)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086880)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086886)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086892)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086899)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086935)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086943)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086982)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087006)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087045)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087048)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087081)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087087)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087106)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087122)
- Terpenoid Backbone Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0121210)
- Ubiquinone Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0002372)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014257)
- Methylhistidine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063638)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063858)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063877)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070060)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070083)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070116)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070126)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070154)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070181)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070208)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070216)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070231)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070236)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070246)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070260)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070267)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070274)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070301)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070325)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070330)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070353)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070380)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070388)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070407)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080512)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080556)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080705)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080724)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080744)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080763)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080792)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080823)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080864)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086781)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086811)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086937)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086989)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087054)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087092)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087094)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087128)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087140)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087152)
- Estrone Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087272)
- Steroid Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0121236)
- Steroid Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0002381)
- Catecholamine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0063606)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063827)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070032)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070183)
- Secondary Metabolites: Ubiquinol Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0121333)
- Cyclopropane Fatty Acid (CFA) Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0122265)
- Mercaptopurine Metabolism Pathway (PathBank: SMP0000609)
- Menaquinol Biosythesis (PathBank: SMP0001911)
- S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine Cycle (PathBank: SMP0002092)
- Methionine Metabolism and Salvage (PathBank: SMP0002310)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria (PathBank: SMP0002424)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER (PathBank: SMP0002425)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism CE(14:0) (PathBank: SMP0002435)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism CE(10:0) (PathBank: SMP0002436)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism CE(12:0) (PathBank: SMP0002438)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism CE(16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002440)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism CE(18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002441)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(16:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002492)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(10:0/10:0) (PathBank: SMP0002512)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(14:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0002513)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(16:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002514)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002515)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(16:1(11Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002516)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(18:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002517)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002518)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(18:2(9Z,11Z)/18:2(9Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002519)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002520)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(10:0/10:0) (PathBank: SMP0002521)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(14:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0002522)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002523)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(16:1(11Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002524)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(18:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002525)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002526)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(18:2(9Z,11Z)/18:2(9Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002527)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002528)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/10:0) (PathBank: SMP0002529)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/12:0) (PathBank: SMP0002530)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0002531)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0002532)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002533)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/12:0) (PathBank: SMP0002534)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0002535)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0002536)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002538)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002540)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/14:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002541)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002542)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/14:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002543)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/14:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002545)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0002547)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002549)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002550)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002551)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002552)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002553)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002554)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002555)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002556)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002557)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002558)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002560)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002561)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002562)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002564)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002565)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002566)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002567)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002568)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/14:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002570)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002571)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/14:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002572)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002573)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002574)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002575)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002576)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002578)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002579)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002580)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002581)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002582)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002583)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002584)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002585)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002586)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002587)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002588)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002591)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002592)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002593)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002596)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002597)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002599)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002600)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002601)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002602)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002603)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002605)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/22:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002606)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/22:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002607)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002608)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002609)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002610)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002614)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002616)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002617)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002618)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002619)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/23:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002620)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/23:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002621)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002622)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002625)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002626)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002627)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002629)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002630)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002633)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002634)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/24:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002635)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/24:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002636)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/22:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002637)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/22:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002638)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002639)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002643)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002647)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002648)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002649)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002650)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002651)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/25:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002652)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/25:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002653)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002654)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/23:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002655)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/23:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002656)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002657)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002660)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002661)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002663)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002664)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/22:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002665)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/22:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002666)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002667)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002669)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002670)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/26:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002677)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/26:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002678)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/24:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002679)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/24:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002680)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002681)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002682)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002683)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0002685)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002689)
- Flavonoid Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012021)
- Flavone and Flavonol Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012025)
- Choline Biosynthesis I (PathBank: SMP0012026)
- Choline Biosynthesis II (PathBank: SMP0012027)
- Phylloquinol Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012040)
- Plastoquinol-9 Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012043)
- Glycine Betaine Biosynthesis I (PathBank: SMP0012047)
- Glycine Betaine Biosynthesis II (PathBank: SMP0012048)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014245)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014274)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014275)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014303)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014304)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014305)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014332)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014333)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014334)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014335)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014361)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014362)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014363)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014364)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014365)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014390)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014391)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014392)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014393)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014394)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014395)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014419)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014420)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014421)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014422)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014423)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014424)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014447)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014448)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014449)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014450)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014451)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014452)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014453)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014454)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014476)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014477)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014478)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014479)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014480)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014481)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014482)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014483)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014484)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014505)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014506)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014507)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014508)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014509)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014510)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014511)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014512)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014513)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014514)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014534)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014535)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014536)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014537)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014538)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014539)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014540)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014541)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014542)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014543)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014544)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014563)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014564)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014565)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014566)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014567)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014568)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014569)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014570)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014571)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014572)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014573)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014574)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014592)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014593)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014594)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014595)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014596)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014597)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014598)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014599)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014600)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014601)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014602)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014603)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014604)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014621)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014622)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014623)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014624)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014625)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014626)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014627)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014628)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014629)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014630)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014631)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014632)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014633)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014634)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014650)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014651)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014652)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014653)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014654)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014655)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014656)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014657)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014658)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014659)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014660)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014661)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014662)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014663)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014664)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014679)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014680)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014681)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014682)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014683)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014684)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014685)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014686)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014687)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014688)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014689)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014690)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014691)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014692)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014693)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014694)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014708)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014709)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014710)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014711)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014712)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014713)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014714)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014715)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014716)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014717)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014718)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014719)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014720)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014721)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014722)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014723)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014724)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014737)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014738)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014739)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014740)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014741)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014742)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014743)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014744)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014745)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014746)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014747)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014748)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014749)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014750)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014751)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014752)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014753)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014754)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014766)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014767)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014768)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014769)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014770)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014771)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014772)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014773)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014774)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014775)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014776)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014777)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014778)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014779)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014780)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014781)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014782)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014783)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014784)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014795)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014796)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014797)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014798)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014799)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014800)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014801)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014802)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014803)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014804)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014805)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014806)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014807)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014808)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014809)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014810)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014811)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014812)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014813)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014814)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014824)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014825)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014826)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014827)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014828)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014829)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014830)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014831)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014832)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014833)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014834)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014835)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014836)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014837)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014838)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014839)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014840)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014842)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014843)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014844)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014853)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014854)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014855)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014856)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014857)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014858)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014859)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014860)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014861)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014862)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014863)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014864)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014865)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014866)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014867)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014868)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014869)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014870)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014871)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014872)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014873)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014874)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014882)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014883)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014884)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014885)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014886)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014887)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014888)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014889)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014890)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014891)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014892)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014893)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014894)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014895)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014896)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014897)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014898)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014899)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014900)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014901)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014902)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014903)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014904)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014911)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014912)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014913)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014914)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014915)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014916)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014917)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014918)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014919)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014920)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014921)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014922)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014923)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014924)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014925)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014926)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014927)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014928)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014929)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014930)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014931)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014932)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014933)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014934)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014940)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014941)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014942)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014943)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014944)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014945)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014946)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014947)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014948)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014949)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014950)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014951)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014952)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014953)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014954)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014955)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014956)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014957)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014958)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014959)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014960)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014961)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014962)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014963)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014964)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014969)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014970)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014971)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014972)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014973)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014974)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014975)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014976)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014977)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014978)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014979)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014980)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014981)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014982)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014983)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014984)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014985)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014986)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014987)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014988)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014989)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014990)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014991)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014992)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014993)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014994)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014998)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014999)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0015000)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0015001)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015002)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0015003)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015004)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015005)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015006)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015007)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015008)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015009)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0015010)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015011)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015012)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015013)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015014)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015015)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015016)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015017)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0015018)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015019)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015020)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015021)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015022)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015023)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015024)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0015027)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015028)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0015029)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0015030)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015031)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0015032)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015033)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015034)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015035)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015036)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015037)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015038)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0015039)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015040)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015041)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015042)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015043)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015044)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015045)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015046)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0015047)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015048)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015049)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015050)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015051)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015052)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015053)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0015054)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030241)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030242)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030243)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030244)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030245)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030246)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030247)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030248)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030249)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030250)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030251)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030252)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030253)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030254)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030255)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030256)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030257)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030258)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030259)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030260)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030261)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030262)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030263)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030264)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030265)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030266)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030267)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030268)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030269)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030270)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030271)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030272)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030273)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030274)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030275)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030276)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030277)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030278)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030279)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030280)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030281)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030282)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030283)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030284)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030285)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030286)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030287)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030288)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030289)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030290)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030291)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030292)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030293)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030294)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030295)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030296)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030297)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030298)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030299)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030300)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030301)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030302)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030303)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030304)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030305)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030306)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030307)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030308)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030309)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030310)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030311)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030312)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030313)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030314)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030315)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030316)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030317)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030318)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030319)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030320)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030321)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063838)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063848)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063857)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063865)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063872)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063878)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063883)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063887)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(13Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063890)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(13Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063891)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063892)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0070041)
- Juvenile Hormone Synthesis (PathBank: SMP0121063)
- Arsenate Detoxification (PathBank: SMP0121123)
Disease pathwayDrug action pathwaySignaling pathway |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 209 - 211 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| S-Adenosylhomocysteine,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@H]1N1C=NC2=C(N)N=CN=C21 | 3555.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O | 3562.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3458.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,1TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 3556.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,1TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3598.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3433.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3515.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)N([C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 3564.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 3494.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3401.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 3441.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3492.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3394.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3439.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3504.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3422.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3446.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3314.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3406.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3444.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O | 3479.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #13 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O | 3414.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #14 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3456.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #15 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3501.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #16 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3406.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #17 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 3447.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #18 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3568.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3338.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3421.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3365.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3408.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3447.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=NC2=C(N)N=CN=C21 | 3476.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@H]1N1C=NC2=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C21 | 3419.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3360.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3309.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3306.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 5393.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3503.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3515.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5339.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3408.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3388.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 5201.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3466.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3396.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 5449.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #13 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3384.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #13 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3375.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #13 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5236.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #14 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3400.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #14 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3447.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #14 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 4954.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #15 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3499.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #15 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3505.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #15 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 5299.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #16 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3409.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #16 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3398.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #16 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4970.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #17 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3552.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #17 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3468.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #17 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 5344.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #18 | C[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 3554.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #18 | C[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 3533.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #18 | C[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 5106.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3380.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3347.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5528.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3404.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3432.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5283.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3395.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3434.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5471.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3379.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3407.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5411.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3416.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3395.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5245.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3463.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3404.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 5472.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3390.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3381.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 5262.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 3406.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 3454.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 4999.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3407.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3384.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4841.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3544.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3467.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #10 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 4894.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O | 3542.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O | 3512.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #11 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O | 4647.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3563.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3471.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #12 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 4694.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3442.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3385.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 5234.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3387.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3331.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4988.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3402.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3415.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 4588.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3484.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3504.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4943.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3412.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3378.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #6 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4545.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3545.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3471.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #7 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4936.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=NC2=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C21 | 3545.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=NC2=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C21 | 3515.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #8 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=NC2=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C21 | 4689.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3408.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3376.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,5TMS,isomer #9 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4499.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3435.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 3344.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 4222.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3550.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3456.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4626.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3549.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3470.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4345.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3586.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3437.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 4333.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3586.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3435.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,6TMS,isomer #5 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 4287.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,7TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3607.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,7TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 3409.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,7TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 4059.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@H]1N1C=NC2=C(N)N=CN=C21 | 3776.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O | 3778.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3719.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,1TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 3799.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,1TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3810.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3893.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3954.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N([C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4018.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3911.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3871.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 3912.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3906.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3862.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3905.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3903.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3878.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,2TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 3884.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3966.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 3991.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 4045.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O | 4145.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #13 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O | 4025.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #14 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 4034.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #15 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4129.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #16 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3992.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #17 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 4065.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #18 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 4192.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 3975.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4012.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3977.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3999.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4046.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H]1N1C=NC2=C(N)N=CN=C21 | 4145.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@H]1N1C=NC2=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C21 | 4028.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,3TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3968.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4072.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3977.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5331.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4314.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4188.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5207.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 4140.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 4101.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #11 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 5104.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4242.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4059.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #12 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5340.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #13 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4120.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #13 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4101.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #13 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5137.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #14 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 4184.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #14 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 4159.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #14 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O | 4896.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #15 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 4309.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #15 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 4180.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #15 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O | 5175.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #16 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4143.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #16 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4117.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #16 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4897.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #17 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 4293.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #17 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 4150.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #17 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O | 5208.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #18 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4352.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #18 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4216.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #18 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(C1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4991.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4130.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4067.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5406.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4170.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4130.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5175.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4249.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4066.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5368.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4156.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4116.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CSCC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5270.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4147.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4107.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2[C@@H]1O[C@H](CSCC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5139.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4242.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4067.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5359.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4120.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4107.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 5159.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 4189.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 4165.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylhomocysteine,4TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N[C@@H](CCSC[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)C(=O)O | 4929.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0a6u-9853000000-441f171739659ea2b5f6 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (3 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-004r-7096060000-d32383fe3b85ef1b9032 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_1_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_6) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_7) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_8) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_9) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_10) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_11) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_2_12) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_3_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_3_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_3_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine GC-MS (TMS_3_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0319020200-859d659a39a790a582f1 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-53acf4e10681047da062 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0910000000-5896502e31d66786e12a | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0009000000-01ea51599f8d30dec7fe | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0409000100-2de58945ab0dfa81f099 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-1900000000-a640f1a0bafd33afdd2d | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0910000000-5f685035af9b243ccff2 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0009000000-8d01fd0969e47d3bcc5c | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0902000000-c6c0d5529cf011d89f7b | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT , negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-53acf4e10681047da062 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT , negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0910000000-5896502e31d66786e12a | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT , negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0009000000-01ea51599f8d30dec7fe | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT , negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-1900000000-a640f1a0bafd33afdd2d | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT , negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0910000000-6da47cc70ea7d7eb41f1 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT , negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0009000000-8d01fd0969e47d3bcc5c | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-QTOF , negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0902000000-c6c0d5529cf011d89f7b | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine 35V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-0900000000-978dc4fcc4643522e8ef | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-0943000000-80fa5c7d919e1085bc5d | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-0900000000-3f143852503952daa0a8 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-23694a4b657a3478ad91 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udr-0980000000-a8f61dcdc8693e2725f5 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-00kf-0974000000-b3f3632635b2847bf4d2 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-0900000000-188a77c79aaefae8a184 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-0900000000-b848c20d743785117445 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylhomocysteine LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udr-0980000000-64b7b303fc07300e0782 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, 100%_DMSO, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, 100%_DMSO, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Mitochondria
- Nucleus
- Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Feces
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Kidney
- Liver
- Neuron
- Placenta
- Prostate
|
|---|
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.46 +/- 0.02 uM | Elderly (>65 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00900-0.0450 uM | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.00100-0.0290 uM | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.01 (0.009-0.014) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0243 +/- 0.0068 uM | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Expected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Available | Not Available | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.016 (0.009-0.025) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Neurodegenerative diseases | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.49 +/- 0.05 uM | Elderly (>65 years old) | Both | Parkinson's Disease | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.102 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Female | Adenosine kinase deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.122 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Adenosine kinase deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0269 +/- 0.0062 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Alzheimer's disease | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.068 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Female | Adenosine kinase deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.102 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Adenosine kinase deficiency | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Enthesitis-related arthritis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.882 +/- 0.075 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Eosinophilic esophagitis | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Parkinson's disease |
|---|
- Cheng H, Gomes-Trolin C, Aquilonius SM, Steinberg A, Lofberg C, Ekblom J, Oreland L: Levels of L-methionine S-adenosyltransferase activity in erythrocytes and concentrations of S-adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylhomocysteine in whole blood of patients with Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol. 1997 Jun;145(2 Pt 1):580-5. [PubMed:9217094 ]
| | Neurodegenerative disease |
|---|
- Obeid R, Kostopoulos P, Knapp JP, Kasoha M, Becker G, Fassbender K, Herrmann W: Biomarkers of folate and vitamin B12 are related in blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem. 2007 Feb;53(2):326-33. Epub 2007 Jan 2. [PubMed:17200133 ]
| | Alzheimer's disease |
|---|
- Linnebank M, Popp J, Smulders Y, Smith D, Semmler A, Farkas M, Kulic L, Cvetanovska G, Blom H, Stoffel-Wagner B, Kolsch H, Weller M, Jessen F: S-adenosylmethionine is decreased in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurodegener Dis. 2010;7(6):373-8. doi: 10.1159/000309657. Epub 2010 Jun 3. [PubMed:20523031 ]
| | Adenosine kinase deficiency |
|---|
- Bjursell MK, Blom HJ, Cayuela JA, Engvall ML, Lesko N, Balasubramaniam S, Brandberg G, Halldin M, Falkenberg M, Jakobs C, Smith D, Struys E, von Dobeln U, Gustafsson CM, Lundeberg J, Wedell A: Adenosine kinase deficiency disrupts the methionine cycle and causes hypermethioninemia, encephalopathy, and abnormal liver function. Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Oct 7;89(4):507-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.09.004. Epub 2011 Sep 28. [PubMed:21963049 ]
| | Eosinophilic esophagitis |
|---|
- Slae, M., Huynh, H., Wishart, D.S. (2014). Analysis of 30 normal pediatric urine samples via NMR spectroscopy (unpublished work). NA.
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 168600 (Parkinson's disease)
- 104300 (Alzheimer's disease)
- 614300 (Adenosine kinase deficiency)
- 610247 (Eosinophilic esophagitis)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB01752 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB031150 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00007230 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 388301 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00021 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | ADENOSYL-HOMO-CYS |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 33543 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 296 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 439155 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 16680 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | AHCYS |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000286 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Holy, Antonin; Rosenberg, Ivan. Studies on S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase. Part XV. An improved synthesis of S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine and related compounds. Collection of Czechoslovak Chemical Communications (1985), 50(7), 1514-18. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) |
|---|
| General References | - Augoustides-Savvopoulou P, Luka Z, Karyda S, Stabler SP, Allen RH, Patsiaoura K, Wagner C, Mudd SH: Glycine N -methyltransferase deficiency: a new patient with a novel mutation. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2003;26(8):745-59. [PubMed:14739680 ]
- Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. doi: 10.1038/nature07762. [PubMed:19212411 ]
- Hershfield MS, Kredich NM, Koller CA, Mitchell BS, Kurtzberg J, Kinney TR, Falletta JM: S-adenosylhomocysteine catabolism and basis for acquired resistance during treatment of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia with 2'-deoxycoformycin alone and in combination with 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. Cancer Res. 1983 Jul;43(7):3451-8. [PubMed:6601986 ]
- Miller AL: The methionine-homocysteine cycle and its effects on cognitive diseases. Altern Med Rev. 2003 Feb;8(1):7-19. [PubMed:12611557 ]
- Struys EA, Jansen EE, de Meer K, Jakobs C: Determination of S-adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylhomocysteine in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid by stable-isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2000 Oct;46(10):1650-6. [PubMed:11017945 ]
- Wang J, Dudman NP, Wilcken DE: Effects of homocysteine and related compounds on prostacyclin production by cultured human vascular endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Dec 20;70(6):1047-52. [PubMed:8165599 ]
- Palella TD, Schatz RA, Wilens TE, Fox IH: S-Adenosylhomocysteine accumulation and selective cytotoxicity in cultured T- and B-lymphocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Aug;100(2):269-78. [PubMed:6980250 ]
- van Guldener C, Stehouwer CD: Homocysteine and methionine metabolism in renal failure. Semin Vasc Med. 2005 May;5(2):201-8. [PubMed:16047272 ]
- Muskiet FA: The importance of (early) folate status to primary and secondary coronary artery disease prevention. Reprod Toxicol. 2005 Sep-Oct;20(3):403-10. [PubMed:15964170 ]
- Fowler B: Homocysteine: overview of biochemistry, molecular biology, and role in disease processes. Semin Vasc Med. 2005 May;5(2):77-86. [PubMed:16047261 ]
- Gordon RK, Ginalski K, Rudnicki WR, Rychlewski L, Pankaskie MC, Bujnicki JM, Chiang PK: Anti-HIV-1 activity of 3-deaza-adenosine analogs. Inhibition of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and nucleotide congeners. Eur J Biochem. 2003 Sep;270(17):3507-17. [PubMed:12919315 ]
- Metz J: Cobalamin deficiency and the pathogenesis of nervous system disease. Annu Rev Nutr. 1992;12:59-79. [PubMed:1354465 ]
- Mulder C, Schoonenboom NS, Jansen EE, Verhoeven NM, van Kamp GJ, Jakobs C, Scheltens P: The transmethylation cycle in the brain of Alzheimer patients. Neurosci Lett. 2005 Sep 30;386(2):69-71. [PubMed:16040194 ]
- Delabar U, Kloor D, Luippold G, Muhlbauer B: Simultaneous determination of adenosine, S-adenosylhomocysteine and S-adenosylmethionine in biological samples using solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1999 Mar 19;724(2):231-8. [PubMed:10219663 ]
- Hermes M, von Hippel S, Osswald H, Kloor D: S-adenosylhomocysteine metabolism in different cell lines: effect of hypoxia and cell density. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2005;15(5):233-44. [PubMed:15956786 ]
- Weir DG, Molloy AM, Keating JN, Young PB, Kennedy S, Kennedy DG, Scott JM: Correlation of the ratio of S-adenosyl-L-methionine to S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid of the pig: implications for the determination of this methylation ratio in human brain. Clin Sci (Lond). 1992 Jan;82(1):93-7. [PubMed:1310924 ]
- Wagner C, Koury MJ: S-Adenosylhomocysteine: a better indicator of vascular disease than homocysteine? Am J Clin Nutr. 2007 Dec;86(6):1581-5. [PubMed:18065573 ]
- Herrmann W, Obeid R: Biomarkers of folate and vitamin B(12) status in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007;45(12):1614-20. [PubMed:17892439 ]
- Kredich NM, Hershfield MS: S-adenosylhomocysteine toxicity in normal and adenosine kinase-deficient lymphoblasts of human origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2450-4. [PubMed:221926 ]
- Elshenawy S, Pinney SE, Stuart T, Doulias PT, Zura G, Parry S, Elovitz MA, Bennett MJ, Bansal A, Strauss JF 3rd, Ischiropoulos H, Simmons RA: The Metabolomic Signature of the Placenta in Spontaneous Preterm Birth. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3). pii: ijms21031043. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031043. [PubMed:32033212 ]
| Show more...
|---|