Showing metabocard for 11-cis-Retinol (HMDB0006216)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 5.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Expected but not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2007-05-22 17:49:55 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:30 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB0006216 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolite Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | 11-cis-Retinol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Cis-11-retinol is produce from vitamin A cycle driven by interphotoreceptor retinoid binding protein(IRBP). cis-11-retinol is released from retinal pigment epithelium(RPE) membranes. (PMID: 10655150 ). Retinoid metabolism of RPE cells freshly isolated by trypsinization showed no 11- cis -retinal and little 11- cis -retinol formation. Nondamaged cells cultured on thermally responsive surfaces detached in sheets upon temperature change. They showed metabolism similar to that of cells freshly isolated by nonenzymatic means. After trypsinization, confluent cultures dissociated into individual cells, but these cells showed poor retinoid metabolism, including no detectable retinyl esters or 11- cis -retinoid isomers. (PMID: 10375454 ). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C20H30O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight | 286.4516 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 286.229665582 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | (2E,4Z,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraen-1-ol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | vitamin a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 22737-96-8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | C\C(=C/CO)\C=C/C=C(\C)/C=C/C1=C(C)CCCC1(C)C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H30O/c1-16(8-6-9-17(2)13-15-21)11-12-19-18(3)10-7-14-20(19,4)5/h6,8-9,11-13,21H,7,10,14-15H2,1-5H3/b9-6-,12-11+,16-8+,17-13+ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | FPIPGXGPPPQFEQ-IOUUIBBYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as retinoids. These are oxygenated derivatives of 3,7-dimethyl-1-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-enyl)nona-1,3,5,7-tetraene and derivatives thereof. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Prenol lipids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Retinoids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Retinoids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ontology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physiological effect | Health effect
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Disposition | Biological location
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Process | Naturally occurring process
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Role | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Molecular Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Molecular Properties |
| Show more...||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross Sections
Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatized
Derivatized
| Show more...||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
GC-MS Spectra
MS/MS Spectra
NMR Spectra
| Show more...|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biospecimen Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
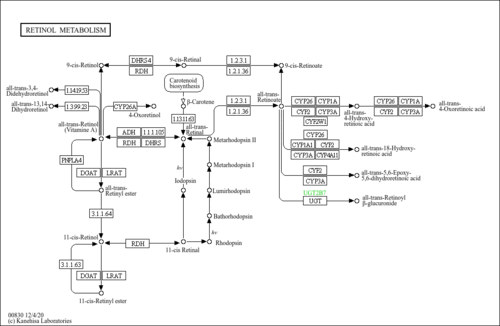
| Pathways | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associated Disorders and Diseases | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Disease References | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associated OMIM IDs | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FooDB ID | FDB023840 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemspider ID | 4444073 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Compound ID | C00899 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | CPD-882 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BiGG ID | 2265508 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METLIN ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound | 5280382 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 16302 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VMH ID | RETINOL_CIS_11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Good Scents ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Brown, Paul K.; Wald, George. The neo-b isomer of vitamin A and retinine. Journal of Biological Chemistry (1956), 222 865-77. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Involved in diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase activity
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the terminal and only committed step in triacylglycerol synthesis by using diacylglycerol and fatty acyl CoA as substrates. In contrast to DGAT2 it is not essential for survival. May be involved in VLDL (very low density lipoprotein) assembly. In liver, plays a role in esterifying exogenous fatty acids to glycerol. Functions as the major acyl-CoA retinol acyltransferase (ARAT) in the skin, where it acts to maintain retinoid homeostasis and prevent retinoid toxicity leading to skin and hair disorders.
- Gene Name:
- DGAT1
- Uniprot ID:
- O75907
- Molecular weight:
- 55277.735
Reactions
| Palmityl-CoA + 11-cis-Retinol → Coenzyme A + 11-cis-Retinyl palmitate | details |
- General function:
- Involved in oxidoreductase activity
- Specific function:
- Stereospecific 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase, which catalyzes the final step in the biosynthesis of 11-cis retinaldehyde, the universal chromophore of visual pigments. Also able to oxidize 9-cis-retinol and 13-cis-retinol, but not all-trans-retinol. Active in the presence of NAD as cofactor but not in the presence of NADP.
- Gene Name:
- RDH5
- Uniprot ID:
- Q92781
- Molecular weight:
- 34978.425
- General function:
- Secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism
- Specific function:
- Plays important roles in the production of 11-cis retinal and in visual pigment regeneration. The soluble form binds vitamin A (all-trans-retinol), making it available for LRAT processing to all-trans-retinyl ester. The membrane form, palmitoylated by LRAT, binds all-trans-retinyl esters, making them available for IMH (isomerohydrolase) processing to all-cis-retinol. The soluble form is regenerated by transferring its palmitoyl groups onto 11-cis-retinol, a reaction catalyzed by LRAT. The enzymatic activity is linearly dependent of the expression levels and membrane association.
- Gene Name:
- RPE65
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16518
- Molecular weight:
- 60947.08
Reactions
| An all-trans-retinyl ester + Water → 11-cis-Retinol + a fatty acid | details |
| Retinyl ester + Water → 11-cis-Retinol + Fatty acid | details |
- General function:
- Involved in phosphatidylcholine-retinol O-acyltransfera
- Specific function:
- Transfers the acyl group from the sn-1 position of phosphatidylcholine to all-trans retinol, producing all-trans retinyl esters. Retinyl esters are storage forms of vitamin A. LRAT plays a critical role in vision. It provides the all-trans retinyl ester substrates for the isomerohydrolase which processes the esters into 11-cis-retinol in the retinal pigment epithelium; due to a membrane-associated alcohol dehydrogenase, 11 cis-retinol is oxidized and converted into 11-cis-retinaldehyde which is the chromophore for rhodopsin and the cone photopigments.
- Gene Name:
- LRAT
- Uniprot ID:
- O95237
- Molecular weight:
- 25702.635
Reactions
| Palmitoylphosphatidylcholine + 11-cis-Retinol → 11-cis-Retinyl palmitate + 2-Acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | details |
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups other than amino-acyl groups
- Specific function:
- Acyltransferase that predominantly esterify long chain (wax) alcohols with acyl-CoA-derived fatty acids to produce wax esters. Wax esters are enriched in sebum, suggesting that it plays a central role in lipid metabolism in skin. Has a preference for arachidyl alcohol as well as decyl alcohol, demonstrating its relatively poor activity using saturated long chain alcohols (C16, C18, and C20).
- Gene Name:
- AWAT1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q58HT5
- Molecular weight:
- 37758.815
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups other than amino-acyl groups
- Specific function:
- Acyltransferase that predominantly esterify long chain (wax) alcohols with acyl-CoA-derived fatty acids to produce wax esters. Wax esters are enriched in sebum, suggesting that it plays a central role in lipid metabolism in skin. Has no activity using decyl alcohol and significantly prefers the C16 and C18 alcohols. May also have 2-acylglycerol O-acyltransferase (MGAT) and acyl-CoA:retinol acyltransferase (ARAT) activities, to catalyze the synthesis of diacylglycerols and retinyl esters; however this activity is unclear in vivo.
- Gene Name:
- AWAT2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6E213
- Molecular weight:
- 38093.25