| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2021-09-07 16:45:30 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0001491 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate |
|---|
| Description | Pyridoxal phosphate, also known as PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate or P5P, is the active form of vitamin B6. It is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyridoxals and derivatives. Pyridoxals and derivatives are compounds containing a pyridoxal moiety, which consists of a pyridine ring substituted at positions 2,3,4, and 5 by a methyl group, a hydroxyl group, a carbaldehyde group, and a hydroxymethyl group, respectively. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate is a drug which is used for nutritional supplementation and for treating dietary shortage or imbalance. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. In humans, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate is involved in glycine and serine metabolism. Outside of the human body, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate is found, on average, in the highest concentration within cow milk. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate has also been detected, but not quantified in several different foods, such as soursops, italian sweet red peppers, muscadine grapes, european plums, and blackcurrants. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, with regard to humans, has been found to be associated with several diseases such as epilepsy, early-onset, vitamin B6-dependent, odontohypophosphatasia, pyridoxamine 5-prime-phosphate oxidase deficiency, and hypophosphatasia. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate has also been linked to the inborn metabolic disorder celiac disease. |
|---|
| Structure | CC1=NC=C(COP(O)(O)=O)C(C=O)=C1O InChI=1S/C8H10NO6P/c1-5-8(11)7(3-10)6(2-9-5)4-15-16(12,13)14/h2-3,11H,4H2,1H3,(H2,12,13,14) |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 3-Hydroxy-2-methyl-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]-4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde | ChEBI | | 3-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylisonicotinaldehyde 5-phosphate | ChEBI | | Codecarboxylase | ChEBI | | Phosphoric acid mono-(4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-pyridin-3-ylmethyl) ester | ChEBI | | PLP | ChEBI | | Pyridoxal 5'-(dihydrogen phosphate) | ChEBI | | Pyridoxal 5-monophosphoric acid ester | ChEBI | | Pyridoxal 5-phosphate | ChEBI | | Pyridoxal phosphate | ChEBI | | PYRIDOXAL-5'-phosphATE | ChEBI | | 3-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylisonicotinaldehyde 5-phosphoric acid | Generator | | Phosphate mono-(4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methyl-pyridin-3-ylmethyl) ester | Generator | | Pyridoxal 5'-(dihydrogen phosphoric acid) | Generator | | Pyridoxal 5-monophosphate ester | Generator | | Pyridoxal 5-phosphoric acid | Generator | | Pyridoxal phosphoric acid | Generator | | PYRIDOXAL-5'-phosphoric acid | Generator | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphoric acid | Generator | | Apolon b6 | HMDB | | Biosechs | HMDB | | Coenzyme b6 | HMDB | | Hairoxal | HMDB | | Hexermin-p | HMDB | | Hi-pyridoxin | HMDB | | Hiadelon | HMDB | | Himitan | HMDB | | PAL-p | HMDB | | Phosphopyridoxal | HMDB | | Phosphopyridoxal coenzyme | HMDB | | Pidopidon | HMDB | | Piodel | HMDB | | Pydoxal | HMDB | | Pyridoxal p | HMDB | | Pyridoxal-p | HMDB | | Pyridoxyl phosphate | HMDB | | Pyromijin | HMDB | | Sechvitan | HMDB | | Vitahexin-p | HMDB | | Vitazechs | HMDB | | Phosphate, pyridoxal | HMDB | | Pyridoxal 5 phosphate | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C8H10NO6P |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 247.1419 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 247.024573569 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | [(4-formyl-5-hydroxy-6-methylpyridin-3-yl)methoxy]phosphonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | pyridoxal phosphate |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 54-47-7 |
|---|
| SMILES | CC1=NC=C(COP(O)(O)=O)C(C=O)=C1O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C8H10NO6P/c1-5-8(11)7(3-10)6(2-9-5)4-15-16(12,13)14/h2-3,11H,4H2,1H3,(H2,12,13,14) |
|---|
| InChI Key | NGVDGCNFYWLIFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyridoxals and derivatives. Pyridoxals and derivatives are compounds containing a pyridoxal moiety, which consists of a pyridine ring substituted at positions 2,3,4, and 5 by a methyl group, a hydroxyl group, a carbaldehyde group, and a hydroxymethyl group, respectively. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Pyridines and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Pyridine carboxaldehydes |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Pyridoxals and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Pyridoxal
- Aryl-aldehyde
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Hydroxypyridine
- Methylpyridine
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Alkyl phosphate
- Vinylogous acid
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Azacycle
- Organopnictogen compound
- Aldehyde
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
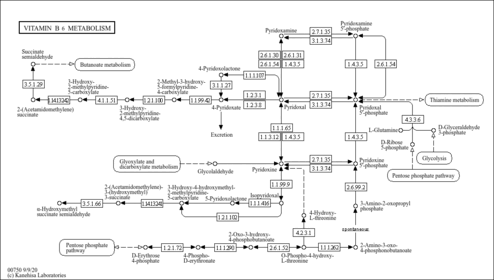
| Process | Naturally occurring processBiological processBiochemical pathwayMetabolic pathway- Glucose-Alanine Cycle (HMDB: HMDB0001491)
- Vitamin B6 Metabolism (HMDB: HMDB0001491)
- Malate-Aspartate Shuttle (HMDB: HMDB0001491)
- Alanine Metabolism (HMDB: HMDB0001491)
- Porphyrin Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0000953)
- Sphingolipid Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0002378)
- Sulfur Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0002382)
- Arginine and Proline Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0012004)
- Vitamin B6 Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063472)
- Ammonia Recycling (PathBank: SMP0063579)
- Alanine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063586)
- Selenoamino Acid Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063587)
- Cysteine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063607)
- Histidine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063632)
- Methionine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063637)
- Sphingolipid Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063667)
- Spermidine and Spermine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0063671)
- Beta-Alanine metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087180)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071724)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0071727)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0071730)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071739)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0071741)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071743)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071769)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071771)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0071772)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071788)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071791)
- Urea Cycle (PathBank: SMP0087224)
- Threonine and 2-Oxobutanoate Degradation (PathBank: SMP0087262)
- Glutamate Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087278)
- Homocysteine Degradation (PathBank: SMP0087298)
- Tyrosine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087328)
- Aspartate Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087369)
- Glycine and Serine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087466)
- Propanoate Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087480)
- Sulfur Metabolism (Ethanesulfonate) (PathBank: SMP0121318)
- Starch and Sucrose Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0000958)
- Taurine and Hypotaurine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063675)
- Valine, Leucine, and Isoleucine Degradation (PathBank: SMP0063689)
- Tryptophan Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063693)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0071721)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071725)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071728)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0071732)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071736)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071746)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071749)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071752)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071754)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071764)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071770)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071773)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071776)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071777)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071787)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(22:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0071795)
- Lysine Degradation (PathBank: SMP0087300)
- Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087313)
- Folate Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087435)
- Cysteine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0121282)
- Porphyrin Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0002363)
- Starch and Sucrose Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0002380)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0071720)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071723)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071731)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071733)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071734)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071735)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0071738)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0071748)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0071751)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071756)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0071757)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071758)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0071760)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0071775)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0071778)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0071783)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(22:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071796)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(22:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071797)
- Carnitine Synthesis (PathBank: SMP0087187)
- Sulfur Metabolism (Butanesulfonate) (PathBank: SMP0121316)
- Sulfur Metabolism (Isethionate) (PathBank: SMP0121319)
- Secondary Metabolites: Trehalose Biosynthesis and Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0121327)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0014205)
- Catecholamine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0063606)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071722)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071726)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071737)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071742)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071744)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071745)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071747)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071753)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071755)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071761)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071762)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071763)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0071765)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071766)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0071768)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071779)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0071781)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071782)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071784)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0071786)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0071790)
- Threonine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0121292)
- Sulfur Metabolism (Propanesulfonate) (PathBank: SMP0121317)
- Sulfur Metabolism (Methanesulfonate) (PathBank: SMP0121320)
- Phenylalanine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0000938)
- Secondary Metabolites: Enterobacterial Common Antigen Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0000975)
- Secondary Metabolites: Enterobacterial Common Antigen Biosynthesis 2 (PathBank: SMP0002059)
- Secondary Metabolites: Enterobacterial Common Antigen Biosynthesis 3 (PathBank: SMP0002060)
- Vitamin B6 (PathBank: SMP0002387)
- Choline Biosynthesis I (PathBank: SMP0012026)
- Choline Biosynthesis II (PathBank: SMP0012027)
- Plastoquinol-9 Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012043)
- Thio-Molybdenum Cofactor Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012046)
- Glycine Betaine Biosynthesis I (PathBank: SMP0012047)
- Glycine Betaine Biosynthesis II (PathBank: SMP0012048)
- Butanoate metabolism (PathBank: SMP0012467)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0014208)
- Isoquinoline Alkaloid Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0063471)
- Tropane, Piperidine, and Pyridine Alkaloid Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0063474)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(16:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071729)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071740)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071750)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071759)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071767)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071774)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071780)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071785)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071789)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:1(13Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071792)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:1(13Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0071793)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine Biosynthesis PE(20:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0071794)
- L-Homomethionine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0121204)
Disease pathway- Hypophosphatasia (HMDB: HMDB0001491)
- Cystinosis, Ocular Nonnephropathic (HMDB: HMDB0001491)
- Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Deficiency (MTHFRD) (PathBank: SMP0000340)
- Glutaminolysis and Cancer (PathBank: SMP0108773)
- Sarcosine Oncometabolite Pathway (PathBank: SMP0108776)
- 2-Methyl-3-hydroxybutryl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120439)
- 4-Hydroxybutyric Aciduria/Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120445)
- Arginine: Glycine Amidinotransferase Deficiency (AGAT Deficiency) (PathBank: SMP0120454)
- Cystathionine beta-Synthase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120471)
- GABA-Transaminase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120478)
- Hereditary Coproporphyria (HCP) (PathBank: SMP0120492)
- Histidinemia (PathBank: SMP0120493)
- Hypermethioninemia (PathBank: SMP0120498)
- Sarcosinemia (PathBank: SMP0120521)
- Methylmalonate Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120523)
- Creatine Deficiency, Guanidinoacetate Methyltransferase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120569)
- Isovaleric Acidemia (PathBank: SMP0120589)
- Glycogenosis, Type III. Cori Disease, Debrancher Glycogenosis (PathBank: SMP0120617)
- Succinic Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120631)
- Pyridoxine Dependency with Seizures (PathBank: SMP0120635)
- 3-Methylglutaconic Aciduria Type I (PathBank: SMP0120663)
- Argininemia (PathBank: SMP0120676)
- Argininosuccinic Aciduria (PathBank: SMP0120677)
- Beta-Ketothiolase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120679)
- Canavan Disease (PathBank: SMP0120681)
- Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120682)
- Congenital Erythropoietic Porphyria (CEP) or Gunther Disease (PathBank: SMP0120689)
- Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase Deficiency (DHPD) (PathBank: SMP0120694)
- Globoid Cell Leukodystrophy (PathBank: SMP0120702)
- Glutaric Aciduria Type I (PathBank: SMP0120704)
- Glycine N-Methyltransferase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120707)
- Hyperprolinemia Type I (PathBank: SMP0120719)
- Hypoacetylaspartia (PathBank: SMP0120722)
- Tyrosinemia Type 3 (TYRO3) (PathBank: SMP0120731)
- Metachromatic Leukodystrophy (MLD) (PathBank: SMP0120738)
- Methionine Adenosyltransferase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120739)
- Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTC Deficiency) (PathBank: SMP0120762)
- Porphyria Variegata (PV) (PathBank: SMP0120764)
- Tyrosinemia, Transient, of the Newborn (PathBank: SMP0120779)
- Beta-Mercaptolactate-Cysteine Disulfiduria (PathBank: SMP0120783)
- Hyperornithinemia with Gyrate Atrophy (HOGA) (PathBank: SMP0120789)
- 3-Hydroxyisobutyric Aciduria (PathBank: SMP0120806)
- Mucopolysaccharidosis VII. Sly Syndrome (PathBank: SMP0120839)
- Sucrase-Isomaltase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120840)
- Homocystinuria-Megaloblastic Anemia Due to Defect in Cobalamin Metabolism, cblG Complementation Type (PathBank: SMP0120853)
- 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase Deficiency Type I (PathBank: SMP0120441)
- 3-Methylglutaconic Aciduria Type IV (PathBank: SMP0120444)
- Aromatic L-Aminoacid Decarboxylase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120457)
- Hyperprolinemia Type II (PathBank: SMP0120501)
- Tyrosinemia Type 2 (or Richner-Hanhart Syndrome) (PathBank: SMP0120513)
- Methylmalonic Aciduria (PathBank: SMP0120525)
- Non-Ketotic Hyperglycinemia (PathBank: SMP0120534)
- Pyruvate Carboxylase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120535)
- Prolinemia Type II (PathBank: SMP0120539)
- Phenylketonuria (PathBank: SMP0120540)
- Prolidase Deficiency (PD) (PathBank: SMP0120541)
- Primary Hyperoxaluria Type I (PathBank: SMP0120543)
- Carnosinuria, Carnosinemia (PathBank: SMP0120558)
- Tyrosine Hydroxylase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120562)
- L-Arginine:Glycine Amidinotransferase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120572)
- Glycogen Synthetase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120616)
- 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA Lyase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120661)
- 3-Methylglutaconic Aciduria Type III (PathBank: SMP0120664)
- Hawkinsinuria (PathBank: SMP0120711)
- Lactic Acidemia (PathBank: SMP0120724)
- Tyrosinemia Type I (PathBank: SMP0120729)
- Methylmalonic Aciduria Due to Cobalamin-Related Disorders (PathBank: SMP0120748)
- Hyperornithinemia-Hyperammonemia-Homocitrullinuria [HHH-syndrome] (PathBank: SMP0120790)
- Gamma-Cystathionase Deficiency (CTH) (PathBank: SMP0120798)
- Krabbe Disease (PathBank: SMP0120810)
- Hyperlysinemia I, Familial (PathBank: SMP0120811)
- Hyperlysinemia II or Saccharopinuria (PathBank: SMP0120812)
- Glycogenosis, Type VI. Hers Disease (PathBank: SMP0120838)
- 2-Aminoadipic 2-Oxoadipic Aciduria (PathBank: SMP0120870)
- 3-Phosphoglycerate Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120872)
- Gaucher Disease (PathBank: SMP0120481)
- Homocarnosinosis (PathBank: SMP0120494)
- Maple Syrup Urine Disease (PathBank: SMP0120516)
- Acute Intermittent Porphyria (PathBank: SMP0120447)
- Alkaptonuria (PathBank: SMP0120453)
- Citrullinemia Type I (PathBank: SMP0120466)
- Propionic Acidemia (PathBank: SMP0120537)
- Ornithine Aminotransferase Deficiency (OAT Deficiency) (PathBank: SMP0120538)
- Dopamine beta-Hydroxylase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120563)
- Isobutyryl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120588)
- 2-Hydroxyglutric Aciduria (D and L Form) (PathBank: SMP0120659)
- Dimethylglycine Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120695)
- Guanidinoacetate Methyltransferase Deficiency (GAMT Deficiency) (PathBank: SMP0120710)
- Isovaleric Aciduria (PathBank: SMP0120723)
- Malonic Aciduria (PathBank: SMP0120734)
- Saccharopinuria/Hyperlysinemia II (PathBank: SMP0120746)
- S-Adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) Hydrolase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120747)
- Hyperglycinemia, Non-Ketotic (PathBank: SMP0120770)
- Malonyl-CoA Decarboxylase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120786)
- Fabry Disease (PathBank: SMP0120809)
- Monoamine Oxidase-A Deficiency (MAO-A) (PathBank: SMP0120817)
- Glycogenosis, Type IV. Amylopectinosis, Anderson Disease (PathBank: SMP0120837)
- Hyperinsulinism-Hyperammonemia Syndrome (PathBank: SMP0120496)
- Homocystinuria, Cystathionine beta-Synthase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120580)
- 3-Hydroxyisobutyric Acid Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0120586)
- Cystinosis, Ocular Nonnephropathic (PathBank: SMP0120654)
- Folate Malabsorption, Hereditary (PathBank: SMP0120656)
- 2-Methyl-3-hydroxybutryl-CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (PathBank: SMP0000137)
- Hyperornithinemia-Hyperammonemia-Homocitrullinuria [HHH-syndrome] (PathBank: SMP0000506)
Drug action pathway- Rheumatoid arthritis (HMDB: HMDB0001491)
|
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 255 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 28 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,1TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O)O)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2203.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,1TMS,isomer #2 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O | 2183.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2256.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2134.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2835.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #2 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O | 2195.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #2 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O | 2144.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TMS,isomer #2 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O | 2744.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2270.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2215.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,3TMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2487.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O)O)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2478.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O | 2420.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2696.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2562.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3020.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O | 2643.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O | 2552.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O | 2949.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2891.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2755.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC1=NC=C(COP(=O)(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(C=O)=C1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2790.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate GC-MS (1 MEOX; 3 TMS) | splash10-0gb9-2690000000-c9bacb7e657461e28407 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0gb9-2690000000-c9bacb7e657461e28407 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-004j-0910000000-0408f3957221fc9882cd | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0gb9-1790000000-b01115fa8b4cfd3612c7 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0002-9520000000-bfd574b2e5355694902a | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-006t-9152000000-26c9f631195663322986 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0f6t-0690000000-4aa57f3f28f0bdef9dcf | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0fxx-8900000000-ee972556340c61650528 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-014l-9100000000-3cc29fb51820adecd59c | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0090000000-9b86e80a9dd0de14ab59 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-03dj-9800000000-9313aa9cbf19bc6311c5 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-9500000000-7ce120a58879e2214ce5 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004j-9200000000-7e6bd8c298613e59fb5d | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-9000000000-4c05178b1645bf01f3fa | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-3920000000-6c5e6106f5658d1d6c50 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-3920000000-f96097815e6922356131 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-002b-9000000000-2c4e243699a95e3a0f88 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Negative-QTOF | splash10-002b-9000000000-8aa111485891af9f0d02 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-0090000000-9b86e80a9dd0de14ab59 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-03dj-9800000000-9313aa9cbf19bc6311c5 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-9500000000-7ce120a58879e2214ce5 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-004j-9200000000-7e6bd8c298613e59fb5d | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-9000000000-4c05178b1645bf01f3fa | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QTOF , negative-QTOF | splash10-002b-9000000000-2c4e243699a95e3a0f88 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate LC-ESI-QTOF , negative-QTOF | splash10-002b-9000000000-8aa111485891af9f0d02 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0f6t-1790000000-1dcb07cd1110c71f7005 | 2015-05-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0900000000-ca6aab7f31a36863a417 | 2015-05-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-9800000000-053802b9c0533d7943ea | 2015-05-26 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0002-9080000000-12ca63d34d39d59f6b42 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-9000000000-144099ec201adbbc4684 | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-9000000000-70a9559d65e78c488e7e | 2015-05-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Erythrocyte
- Kidney
- Liver
- Neuron
- Skeletal Muscle
|
|---|
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0146-0.0728 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.046 (0.035-0.06) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.042 (0.0076-1.26) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0572 +/- 0.0193 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0581 +/- 0.0176 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.205 +/- 0.193 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.030 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.061 +/- 0.052 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.056 +/- 0.042 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.068 +/- 0.015 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.075 +/- 0.022 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0451 (0.00400-0.207) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0047 +/- 0.00072 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0110-0.0340 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0515 +/- 0.0166 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0431 +/- 0.0193 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0305 +/- 0.0111 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0207 +/- 0.0069 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0654 +/- 0.0173 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0531 +/- 0.0186 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0312 +/- 0.0049 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.032-0.078 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.044-0.089 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.000972 +/- 0.000283 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.59 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Female | Odontohypophosphatasia | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.024 (0.019-0.031) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Rheumatoid arthritis | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.251 (0.0310-1.182) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Hypophosphatasia, infantile | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.064 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Truncus arteriosus, seizures and dystonia | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.00243 +/- 0.00138 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | celiac disease | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0119 (0.0036-0.018) uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Not Specified | PNPO deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0036 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Not Specified | PNPO deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.012 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Not Specified | PNPO deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.014 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Not Specified | PNPO deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.018 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Not Specified | PNPO deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.00500-0.00600 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Female | Epilepsy, early-onset, vitamin B6-dependent | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Rheumatoid arthritis |
|---|
- Chiang EP, Smith DE, Selhub J, Dallal G, Wang YC, Roubenoff R: Inflammation causes tissue-specific depletion of vitamin B6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(6):R1254-62. Epub 2005 Sep 13. [PubMed:16277678 ]
| | Hypophosphatasia |
|---|
- Chodirker BN, Coburn SP, Seargeant LE, Whyte MP, Greenberg CR: Increased plasma pyridoxal-5'-phosphate levels before and after pyridoxine loading in carriers of perinatal/infantile hypophosphatasia. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1990;13(6):891-6. [PubMed:2079838 ]
| | Odontohypophosphatasia |
|---|
- Haliloglu B, Guran T, Atay Z, Abali S, Mornet E, Bereket A, Turan S: Infantile loss of teeth: odontohypophosphatasia or childhood hypophosphatasia. Eur J Pediatr. 2013 Jun;172(6):851-3. doi: 10.1007/s00431-012-1868-4. Epub 2012 Oct 24. [PubMed:23093139 ]
| | Celiac disease |
|---|
- Hallert C, Allenmark S, Larsson-Cohn U, Sedvall G: High level of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate in the cerebrospinal fluid of adult celiac patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982 Nov;36(5):851-4. [PubMed:6182788 ]
| | Pyridoxamine 5-prime-phosphate oxidase deficiency |
|---|
- Ormazabal A, Oppenheim M, Serrano M, Garcia-Cazorla A, Campistol J, Ribes A, Ruiz A, Moreno J, Hyland K, Clayton P, Heales S, Artuch R: Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate values in cerebrospinal fluid: reference values and diagnosis of PNPO deficiency in paediatric patients. Mol Genet Metab. 2008 Jun;94(2):173-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2008.01.004. Epub 2008 Feb 21. [PubMed:18294893 ]
| | Epilepsy, early-onset, vitamin B6-dependent |
|---|
- Darin N, Reid E, Prunetti L, Samuelsson L, Husain RA, Wilson M, El Yacoubi B, Footitt E, Chong WK, Wilson LC, Prunty H, Pope S, Heales S, Lascelles K, Champion M, Wassmer E, Veggiotti P, de Crecy-Lagard V, Mills PB, Clayton PT: Mutations in PROSC Disrupt Cellular Pyridoxal Phosphate Homeostasis and Cause Vitamin-B6-Dependent Epilepsy. Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Dec 1;99(6):1325-1337. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.10.011. [PubMed:27912044 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 180300 (Rheumatoid arthritis)
- 241500 (Hypophosphatasia)
- 146300 (Odontohypophosphatasia)
- 212750 (Celiac disease)
- 610090 (Pyridoxamine 5-prime-phosphate oxidase deficiency)
- 617290 (Epilepsy, early-onset, vitamin B6-dependent)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00114 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB021820 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00007503 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 1022 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00018 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | PYRIDOXAL_PHOSPHATE |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 33526 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Pyridoxal_phosphate |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 6275 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 1051 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 18405 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | PYDX5P |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000331 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Huang YC, Lan PH, Cheng CH, Lee BJ, Kan MN: Vitamin B6 intakes and status of mechanically ventilated critically ill patients in Taiwan. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2002 May;56(5):387-92. [PubMed:12001008 ]
- Huang YC, Chang HH, Huang SC, Cheng CH, Lee BJ, Cheng SY, Su KH: Plasma pyridoxal 5'-phosphate is a significant indicator of immune responses in the mechanically ventilated critically ill. Nutrition. 2005 Jul-Aug;21(7-8):779-85. [PubMed:15975484 ]
- Huang YC, Chang SJ, Chiu YT, Chang HH, Cheng CH: The status of plasma homocysteine and related B-vitamins in healthy young vegetarians and nonvegetarians. Eur J Nutr. 2003 Apr;42(2):84-90. [PubMed:12638029 ]
- Chiang EP, Selhub J, Bagley PJ, Dallal G, Roubenoff R: Pyridoxine supplementation corrects vitamin B6 deficiency but does not improve inflammation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(6):R1404-11. Epub 2005 Oct 14. [PubMed:16277693 ]
- Chiang EP, Bagley PJ, Roubenoff R, Nadeau M, Selhub J: Plasma pyridoxal 5'-phosphate concentration is correlated with functional vitamin B-6 indices in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and marginal vitamin B-6 status. J Nutr. 2003 Apr;133(4):1056-9. [PubMed:12672918 ]
- Heiskanen K, Kallio M, Salmenpera L, Siimes MA, Ruokonen I, Perheentupa J: Vitamin B-6 status during childhood: tracking from 2 months to 11 years of age. J Nutr. 1995 Dec;125(12):2985-92. [PubMed:7500176 ]
- Longhi RC, Fleisher LD, Tallan HH, Gaull GE: Cystathionine beta-synthase deficiency: a qualitative abnormality of the deficient enzyme modified by vitamin B6 therapy. Pediatr Res. 1977 Feb;11(2):100-3. [PubMed:840498 ]
- Fonda ML: Vitamin B6 metabolism and binding to proteins in the blood of alcoholic and nonalcoholic men. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1993 Dec;17(6):1171-8. [PubMed:8116826 ]
- Lee BJ, Huang MC, Chung LJ, Cheng CH, Lin KL, Su KH, Huang YC: Folic acid and vitamin B12 are more effective than vitamin B6 in lowering fasting plasma homocysteine concentration in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2004 Mar;58(3):481-7. [PubMed:14985687 ]
- Schuster K, Bailey LB, Cerda JJ, Gregory JF 3rd: Urinary 4-pyridoxic acid excretion in 24-hour versus random urine samples as a measurement of vitamin B6 status in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984 Mar;39(3):466-70. [PubMed:6695847 ]
- Heiskanen K, Siimes MA, Perheentupa J, Salmenpera L: Reference ranges for erythrocyte pyridoxal 5'-phosphate concentration and the erythrocyte aspartate transaminase stimulation test in lactating mothers and their infants. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994 Jun;59(6):1297-303. [PubMed:8198054 ]
- Selvaag E, Bohmer T, Benkestock K: Reduced serum concentrations of riboflavine and ascorbic acid, and blood thiamine pyrophosphate and pyridoxal-5-phosphate in geriatric patients with and without pressure sores. J Nutr Health Aging. 2002;6(1):75-7. [PubMed:11813090 ]
- Iqbal SJ, Plaha DS, Linforth GH, Dalgleish R: Hypophosphatasia: diagnostic application of linked DNA markers in the dominantly inherited adult form. Clin Sci (Lond). 1999 Jul;97(1):73-8. [PubMed:10369796 ]
- Heiskanen K, Siimes MA, Salmenpera L, Perheentupa J: Low vitamin B6 status associated with slow growth in healthy breast-fed infants. Pediatr Res. 1995 Nov;38(5):740-6. [PubMed:8552443 ]
- Chiang EP, Bagley PJ, Selhub J, Nadeau M, Roubenoff R: Abnormal vitamin B(6) status is associated with severity of symptoms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 2003 Mar;114(4):283-7. [PubMed:12681455 ]
- Lacour B, Parry C, Drueke T, Touam M, Kreis H, Bailly M, Durand D: Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate deficiency in uremic undialyzed, hemodialyzed, and non-uremic kidney transplant patients. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jan 24;127(2):205-15. [PubMed:6337752 ]
- Seki T: Combination treatment of high-dose pyridoxal phosphate and low-dose ACTH in children with West syndrome and related disorders. Jpn J Psychiatry Neurol. 1990 Jun;44(2):219-37. [PubMed:1701836 ]
- Akopov MA, Kagan ZS, Berezov TT, Filiptsev PIa: [Kinetics and thermodynamics of heat inactivation of L-threonine-L-serine dehydratase from human liver]. Biokhimiia. 1978 Nov;43(11):2027-32. [PubMed:737218 ]
- Descombes E, Hanck AB, Fellay G: Water soluble vitamins in chronic hemodialysis patients and need for supplementation. Kidney Int. 1993 Jun;43(6):1319-28. [PubMed:8315945 ]
- Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Albanes D, Nieto FJ, Hartman TJ, Tangrea JA, Rautalahti M, Sehlub J, Virtamo J, Taylor PR: Pancreatic cancer risk and nutrition-related methyl-group availability indicators in male smokers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999 Mar 17;91(6):535-41. [PubMed:10088624 ]
| Show more...
|---|