| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Expected but not Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:49:09 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0001374 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0002296
- HMDB01374
- HMDB02296
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Choloyl-CoA |
|---|
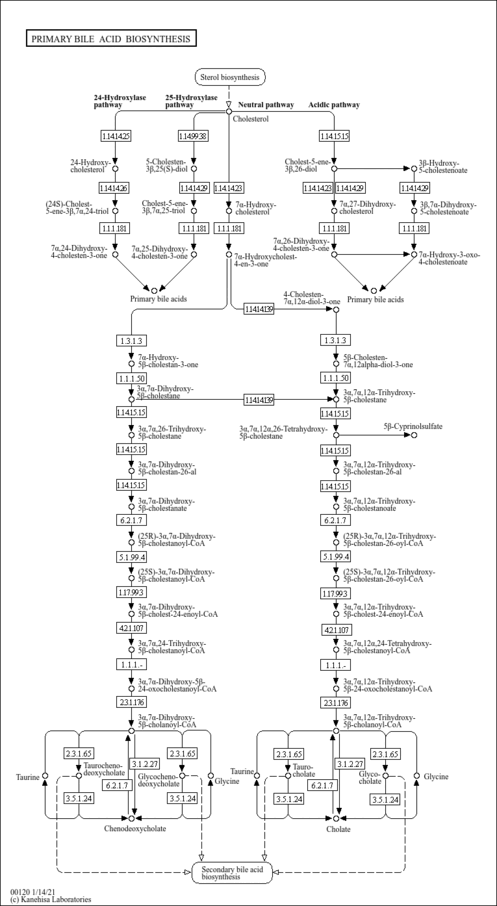
| Description | Choloyl-CoA is an intermediate metabolite in the Bile acid biosynthesis (KEGG). The conjugation of bile acids to glycine and taurine for excretion into bile occurs via a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme Bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase (BACAT) catalyzes. |
|---|
| Structure | [H][C@@]12CCC(C(C)CCC(=O)SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)C(O)C(C)(C)COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]3O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]3OP(O)(O)=O)N3C=NC4=C3N=CN=C4N)C1(C)[C@@H](O)C[C@@]1([H])C2[C@H](O)CC2C[C@H](O)CCC12C InChI=1S/C45H74N7O20P3S/c1-23(26-7-8-27-34-28(18-31(55)45(26,27)5)44(4)12-10-25(53)16-24(44)17-29(34)54)6-9-33(57)76-15-14-47-32(56)11-13-48-41(60)38(59)43(2,3)20-69-75(66,67)72-74(64,65)68-19-30-37(71-73(61,62)63)36(58)42(70-30)52-22-51-35-39(46)49-21-50-40(35)52/h21-31,34,36-38,42,53-55,58-59H,6-20H2,1-5H3,(H,47,56)(H,48,60)(H,64,65)(H,66,67)(H2,46,49,50)(H2,61,62,63)/t23?,24?,25-,26?,27+,28+,29-,30-,31+,34?,36-,37-,38?,42-,44?,45?/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 7-alpha-12-alpha-Dihydroxy-3-oxo-5-beta-cholyl-CoA | HMDB | | Choloyl-coenzyme A | HMDB | | Cholyl-CoA | HMDB | | Cholyl-coenzyme A | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C45H74N7O20P3S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 1158.09 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 1157.392218069 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | {[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-2-({[hydroxy({[hydroxy({3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-3-[(2-{[2-({4-[(1S,5R,9R,11S,16S)-5,9,16-trihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0²,⁷.0¹¹,¹⁵]heptadecan-14-yl]pentanoyl}sulfanyl)ethyl]carbamoyl}ethyl)carbamoyl]propoxy})phosphoryl]oxy})phosphoryl]oxy}methyl)oxolan-3-yl]oxy}phosphonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | [(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-2-[({hydroxy[hydroxy(3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-3-[(2-{[2-({4-[(1S,5R,9R,11S,16S)-5,9,16-trihydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0²,⁷.0¹¹,¹⁵]heptadecan-14-yl]pentanoyl}sulfanyl)ethyl]carbamoyl}ethyl)carbamoyl]propoxy)phosphoryl]oxyphosphoryl}oxy)methyl]oxolan-3-yl]oxyphosphonic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]12CCC(C(C)CCC(=O)SCCNC(=O)CCNC(=O)C(O)C(C)(C)COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]3O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]3OP(O)(O)=O)N3C=NC4=C3N=CN=C4N)C1(C)[C@@H](O)C[C@@]1([H])C2[C@H](O)CC2C[C@H](O)CCC12C |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C45H74N7O20P3S/c1-23(26-7-8-27-34-28(18-31(55)45(26,27)5)44(4)12-10-25(53)16-24(44)17-29(34)54)6-9-33(57)76-15-14-47-32(56)11-13-48-41(60)38(59)43(2,3)20-69-75(66,67)72-74(64,65)68-19-30-37(71-73(61,62)63)36(58)42(70-30)52-22-51-35-39(46)49-21-50-40(35)52/h21-31,34,36-38,42,53-55,58-59H,6-20H2,1-5H3,(H,47,56)(H,48,60)(H,64,65)(H,66,67)(H2,46,49,50)(H2,61,62,63)/t23?,24?,25-,26?,27+,28+,29-,30-,31+,34?,36-,37-,38?,42-,44?,45?/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | ZKWNOTQHFKYUNU-TVKZAFKCSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 2,3,4-saturated fatty acyl coas. These are acyl-CoAs carrying a 2,3,4-saturated fatty acyl chain. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Fatty acyl thioesters |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 2,3,4-saturated fatty acyl CoAs |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Coenzyme a or derivatives
- Steroidal glycoside
- Purine ribonucleoside diphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphate
- Trihydroxy bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- Hydroxy bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- Cholane-skeleton
- Bile acid, alcohol, or derivatives
- 7-hydroxysteroid
- 12-hydroxysteroid
- 3-alpha-hydroxysteroid
- 3-hydroxysteroid
- Hydroxysteroid
- Steroid
- Pentose-5-phosphate
- Ribonucleoside 3'-phosphate
- Pentose phosphate
- Beta amino acid or derivatives
- Glycosyl compound
- N-glycosyl compound
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Organic pyrophosphate
- 6-aminopurine
- Pentose monosaccharide
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Purine
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Aminopyrimidine
- Pyrimidine
- Monosaccharide
- N-acyl-amine
- N-substituted imidazole
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Alkyl phosphate
- Fatty amide
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Imidolactam
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Imidazole
- Cyclic alcohol
- Azole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Carboxamide group
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Secondary alcohol
- Carbothioic s-ester
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Thiocarboxylic acid ester
- Sulfenyl compound
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Thiocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Polyol
- Azacycle
- Oxacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Amine
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Primary amine
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Alcohol
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesNot Available | Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | Not Available | 2022-08-06 | Not Available | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0079-1900011000-f4ca49b8359a4d09e07e | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-0900215000-9d559a6e5a3a263491b9 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-1900001000-711b702e0d30d5413aca | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-055r-2902140210-d19f678a1a85488ae7f7 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-001i-3901120010-0ae33197ae569f3c329e | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-057i-5900100000-d8586a14f0ff3e9b85ba | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0abc-0900000000-0aaaf79d9fb86c2fab0e | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00dr-0900000000-cb368687f92def5847f3 | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0000019000-ae74dd63184feeb2fb1b | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-d2d77d1d1d55961882aa | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4r-2900201100-e76a5ff35442583c5410 | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Choloyl-CoA 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0ar9-5904701700-53d6f0e34697820219bd | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | None |
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | None |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB022586 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 388658 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C01794 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 38424 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 6597 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 439573 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 15519 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | CHOLCOA |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|