| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2021-09-14 15:46:19 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0001185 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0062709
- HMDB01185
- HMDB62709
|
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | S-Adenosylmethionine |
|---|
| Description | S-Adenosylmethionine (CAS: 29908-03-0), also known as SAM or AdoMet, is a physiologic methyl radical donor involved in enzymatic transmethylation reactions and present in all living organisms. It possesses anti-inflammatory activity and has been used in the treatment of chronic liver disease (From Merck, 11th ed). S-Adenosylmethionine is a natural substance present in the cells of the body. It plays a crucial biochemical role by donating a one-carbon methyl group in a process called transmethylation. S-Adenosylmethionine, formed from the reaction of L-methionine and adenosine triphosphate catalyzed by the enzyme S-adenosylmethionine synthetase, is the methyl-group donor in the biosynthesis of both DNA and RNA nucleic acids, phospholipids, proteins, epinephrine, melatonin, creatine, and other molecules. |
|---|
| Structure | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(O)=O)C[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N InChI=1S/C15H22N6O5S/c1-27(3-2-7(16)15(24)25)4-8-10(22)11(23)14(26-8)21-6-20-9-12(17)18-5-19-13(9)21/h5-8,10-11,14,22-23H,2-4,16H2,1H3,(H2-,17,18,19,24,25)/p+1/t7-,8+,10+,11+,14+,27?/m0/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (3S)-5'-[(3-Amino-3-carboxypropyl)methylsulfonio]-5'-deoxyadenosine, inner salt | ChEBI | | [1-(Adenin-9-yl)-1,5-dideoxy-beta-D-ribofuranos-5-yl][(3S)-3-amino-3-carboxypropyl](methyl)sulfonium | ChEBI | | Acylcarnitine | ChEBI | | AdoMet | ChEBI | | S-(5'-Deoxyadenosin-5'-yl)-L-methionine | ChEBI | | SAM | ChEBI | | SAMe | ChEBI | | (3S)-5'-[(3-Amino-3-carboxypropyl)methylsulphonio]-5'-deoxyadenosine, inner salt | Generator | | [1-(Adenin-9-yl)-1,5-dideoxy-b-D-ribofuranos-5-yl][(3S)-3-amino-3-carboxypropyl](methyl)sulfonium | Generator | | [1-(Adenin-9-yl)-1,5-dideoxy-b-D-ribofuranos-5-yl][(3S)-3-amino-3-carboxypropyl](methyl)sulphonium | Generator | | [1-(Adenin-9-yl)-1,5-dideoxy-beta-D-ribofuranos-5-yl][(3S)-3-amino-3-carboxypropyl](methyl)sulphonium | Generator | | [1-(Adenin-9-yl)-1,5-dideoxy-β-D-ribofuranos-5-yl][(3S)-3-amino-3-carboxypropyl](methyl)sulfonium | Generator | | [1-(Adenin-9-yl)-1,5-dideoxy-β-D-ribofuranos-5-yl][(3S)-3-amino-3-carboxypropyl](methyl)sulphonium | Generator | | (3S)-5'-[(3-Amino-3-carboxypropyl)methylsulfonio]-5'-deoxyadenosine | HMDB | | 2-S-Adenosyl-L-methionine | HMDB | | 5'-Deoxyadenosine-5'-L-methionine disulfate ditosylate | HMDB | | 5'-Deoxyadenosine-5'-L-methionine disulphate ditosylate | HMDB | | Active methionine | HMDB | | Ademetionine | HMDB | | Adenosylmethionine | HMDB | | Donamet | HMDB | | L-S-Adenosylmethionine | HMDB | | S-(5'-Adenosyl)-L-methionine | HMDB | | S-Adenosyl methionine | HMDB | | S-Adenosyl-L-methionine | HMDB | | S-Adenosyl-L-methionine disulfate tosylate | HMDB | | S-Adenosyl-L-methionine disulphate tosylate | HMDB | | S-Adenosyl-methionine | HMDB | | ASTA medica brand OF ademetionine tosilate disulfate | HMDB | | S Adenosylmethionine sulfate tosylate | HMDB | | S-Adenosylmethionine sulfate tosylate | HMDB | | Sulfate tosylate, S-adenosylmethionine | HMDB | | Ademetionine europharma brand | HMDB | | Amet, S | HMDB | | Europharma brand OF ademetionine | HMDB | | Gumbaral | HMDB | | Knoll brand OF brand OF ademetionine tosilate disulfate | HMDB | | S Adenosylmethionine | HMDB | | S Amet | HMDB | | Samyr | HMDB | | Tosylate, S-adenosylmethionine sulfate | HMDB | | S Adenosyl L methionine | HMDB | | SAM-e | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C15H23N6O5S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 399.445 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 399.145063566 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | [(3S)-3-amino-3-carboxypropyl]({[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl})methylsulfanium |
|---|
| Traditional Name | SAMe |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 485-80-3 |
|---|
| SMILES | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(O)=O)C[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C15H22N6O5S/c1-27(3-2-7(16)15(24)25)4-8-10(22)11(23)14(26-8)21-6-20-9-12(17)18-5-19-13(9)21/h5-8,10-11,14,22-23H,2-4,16H2,1H3,(H2-,17,18,19,24,25)/p+1/t7-,8+,10+,11+,14+,27?/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | MEFKEPWMEQBLKI-AIRLBKTGSA-O |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 5'-deoxy-5'-thionucleosides. These are 5'-deoxyribonucleosides in which the ribose is thio-substituted at the 5'position by a S-alkyl group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues |
|---|
| Class | 5'-deoxyribonucleosides |
|---|
| Sub Class | 5'-deoxy-5'-thionucleosides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 5'-deoxy-5'-thionucleosides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 5'-deoxy-5'-thionucleoside
- Methionine or derivatives
- N-glycosyl compound
- Glycosyl compound
- Pentose monosaccharide
- 6-aminopurine
- Alpha-amino acid
- L-alpha-amino acid
- Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Purine
- Aminopyrimidine
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Thia fatty acid
- N-substituted imidazole
- Fatty acyl
- Monosaccharide
- Imidolactam
- Pyrimidine
- Azole
- Imidazole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Amino acid or derivatives
- 1,2-diol
- Amino acid
- Secondary alcohol
- Oxacycle
- Azacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary amine
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Amine
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic cation
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
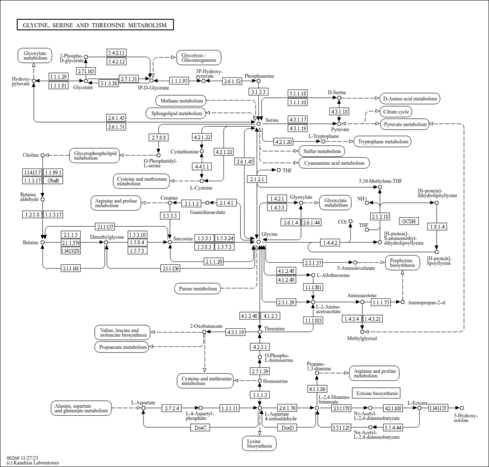
| Process | Naturally occurring processBiological processBiochemical pathwayMetabolic pathway- Glycine and Serine Metabolism (HMDB: HMDB0001185)
- Carnitine Synthesis (HMDB: HMDB0001185)
- Catecholamine Biosynthesis (HMDB: HMDB0001185)
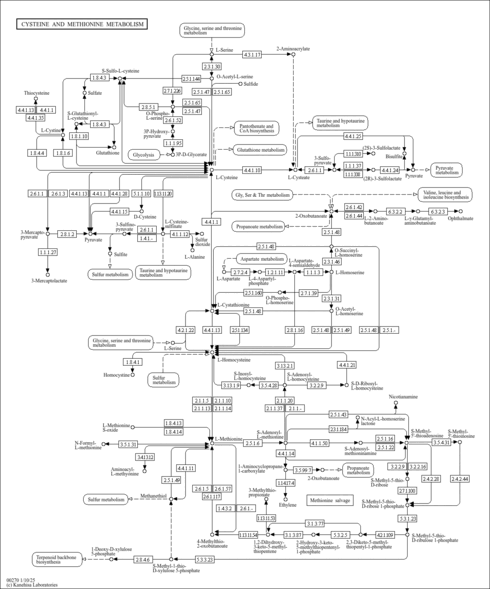
- Methionine Metabolism (HMDB: HMDB0001185)
- Betaine Metabolism (HMDB: HMDB0001185)
- Spermidine and Spermine Biosynthesis (HMDB: HMDB0001185)
- Lipoic Acid Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0121070)
- Porphyrin Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0121321)
- PreQ0 Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0122104)
- Arginine and Proline Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0012004)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0014212)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014219)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014221)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014250)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014258)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014278)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014280)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014307)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014316)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014338)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014366)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014367)
- Histidine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063632)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0063808)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063822)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063831)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063834)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063835)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0063836)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063844)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0063846)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063849)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063866)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063867)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0063870)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063884)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063888)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069980)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069983)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069986)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069987)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069996)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070008)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0070011)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070015)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070018)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070022)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070023)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070024)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070043)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070046)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070058)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070065)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070072)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070073)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070078)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070088)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070089)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070090)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070102)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070110)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070123)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070132)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070133)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070136)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070139)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070140)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070143)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070146)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070148)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070150)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070153)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070157)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070160)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070170)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070175)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070178)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070192)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070196)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070204)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070207)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070214)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070217)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070225)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070235)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070237)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070239)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070243)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070244)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070253)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070255)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070256)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070266)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070270)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070285)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070286)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070292)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070294)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070299)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070300)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070311)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070312)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070314)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070316)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070317)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070318)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070319)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070336)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070337)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070339)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070340)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070343)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070347)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070350)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070355)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070358)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070360)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070365)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070366)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070381)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070382)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070384)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070389)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070390)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070392)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070396)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070397)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070398)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070399)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070402)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070406)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070409)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080467)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070411)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070412)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070415)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080443)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080446)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080449)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080450)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080451)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080452)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080453)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080457)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080469)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080479)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080485)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0080490)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080493)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080498)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080511)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080525)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080528)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080529)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080530)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080533)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080549)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080552)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080554)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080562)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080563)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080568)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080573)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080577)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080579)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080585)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080589)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080592)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080595)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080599)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080609)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080615)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080616)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080627)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080632)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080634)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080636)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080639)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080643)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080645)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080657)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080659)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080667)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080668)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080672)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080674)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080690)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080695)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080697)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080699)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080706)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080713)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080716)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080721)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080723)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080726)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080727)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080729)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080731)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080737)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080745)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080750)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080751)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080752)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080755)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080756)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080758)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080771)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080775)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080776)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080777)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080780)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080782)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080783)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080790)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080799)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080820)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080821)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080826)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080833)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080834)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080843)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080849)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080853)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080854)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080866)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086740)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086742)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0086743)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086745)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086756)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086765)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086767)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086777)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086782)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0086798)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086800)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086803)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086805)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086823)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086828)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086835)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086836)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086847)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086854)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086858)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086882)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0086918)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086922)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086934)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086941)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086946)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086948)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086963)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0086966)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086967)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0086979)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086995)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087002)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087015)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087020)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087022)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087024)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0087025)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087030)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087032)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087052)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087066)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087083)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087107)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087110)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087115)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087118)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087123)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0087124)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087125)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087129)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087131)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087135)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087137)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087144)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087148)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087170)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087188)
- Ubiquinone Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0087215)
- Tyrosine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087328)
- Secondary Metabolites: Ubiquinol Biosynthesis 2 (PathBank: SMP0122225)
- Lipoate Biosynthesis and Incorporation I (PathBank: SMP0122263)
- Biotin Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0000785)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014222)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014249)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014277)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014308)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014309)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014337)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014339)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014344)
- Nicotinate and Nicotinamide Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063643)
- Tryptophan Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063693)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063820)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063842)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063875)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063880)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069989)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0069994)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070004)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070006)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070009)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0070010)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070047)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070054)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070084)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070111)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070127)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070135)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070149)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070159)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070171)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070212)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070215)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070223)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070240)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070248)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070252)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070277)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070280)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070282)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070298)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070309)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070313)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070324)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070338)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070341)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070371)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0070400)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070413)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0080430)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080448)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080477)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080483)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080484)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080486)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0080487)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080500)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080506)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080508)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080523)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080546)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080547)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080561)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080590)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080600)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080604)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080606)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080611)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080620)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080637)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080638)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080641)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080642)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080648)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080649)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080651)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080661)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080670)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0080677)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080680)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080681)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080698)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080710)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080738)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080743)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080754)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080769)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080796)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080800)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080804)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080807)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080817)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080825)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080842)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080857)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0086733)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086776)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0086779)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086795)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086802)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0086806)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086840)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086845)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086856)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086860)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086863)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086880)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086886)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086892)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086899)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086935)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086943)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086982)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087006)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087045)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087048)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087081)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087087)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087106)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087122)
- Terpenoid Backbone Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0121210)
- Spermidine Biosynthesis I (PathBank: SMP0122229)
- Beta-Alanine metabolism (PathBank: SMP0002307)
- Ubiquinone Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0002372)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014257)
- Methylhistidine Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0063638)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063858)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063877)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070060)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070083)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070116)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070126)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070154)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070181)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070208)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070216)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070231)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070236)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070246)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070260)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070267)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070274)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070301)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070325)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070330)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0070353)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070380)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070388)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070407)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080512)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0080556)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080705)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080724)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/24:1(15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080744)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080763)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080792)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0080823)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0080864)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086781)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086811)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086937)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0086989)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087054)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087092)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087094)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087128)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0087140)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0087152)
- Estrone Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0087272)
- Steroid Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0121236)
- S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0121301)
- Steroid Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0002381)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063827)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070032)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0070183)
- Secondary Metabolites: Ubiquinol Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0121333)
- Thiamin Diphosphate Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0122222)
- Cyclopropane Fatty Acid (CFA) Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0122265)
- Mercaptopurine Metabolism Pathway (PathBank: SMP0000609)
- Tyrosine Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0000826)
- Menaquinol Biosythesis (PathBank: SMP0001911)
- Thiazole Biosynthesis I (PathBank: SMP0002055)
- S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine Cycle (PathBank: SMP0002092)
- Spermidine Biosynthesis and Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0002097)
- Methionine Metabolism and Salvage (PathBank: SMP0002310)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria (PathBank: SMP0002424)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER (PathBank: SMP0002425)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism CE(14:0) (PathBank: SMP0002435)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism CE(10:0) (PathBank: SMP0002436)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism CE(12:0) (PathBank: SMP0002438)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism CE(16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002440)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism CE(18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002441)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(16:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002492)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(10:0/10:0) (PathBank: SMP0002512)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(14:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0002513)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(16:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002514)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002515)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(16:1(11Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002516)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(18:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002517)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002518)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(18:2(9Z,11Z)/18:2(9Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002519)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into ER PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002520)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(10:0/10:0) (PathBank: SMP0002521)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(14:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0002522)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(16:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002523)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(16:1(11Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002524)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(18:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002525)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(18:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002526)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(18:2(9Z,11Z)/18:2(9Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002527)
- Lysolipid Incorporation into Mitochondria PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002528)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/10:0) (PathBank: SMP0002529)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/12:0) (PathBank: SMP0002530)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0002531)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0002532)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002533)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/12:0) (PathBank: SMP0002534)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0002535)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0002536)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002538)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002540)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/14:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002541)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002542)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/14:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002543)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/14:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002545)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0002547)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002549)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002550)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002551)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002552)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002553)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002554)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002555)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002556)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002557)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002558)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002560)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002561)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002562)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002564)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002565)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002566)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002567)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002568)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/14:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002570)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002571)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/14:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002572)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002573)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002574)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002575)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002576)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002578)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002579)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002580)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002581)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002582)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/15:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002583)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/15:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002584)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002585)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002586)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002587)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002588)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002591)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002592)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0002593)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002596)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002597)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002599)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002600)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002601)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002602)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002603)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/16:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002605)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/22:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002606)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/22:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002607)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002608)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002609)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002610)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002614)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002616)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002617)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002618)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002619)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/23:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002620)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/23:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002621)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002622)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002625)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002626)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002627)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002629)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002630)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002633)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002634)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/24:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002635)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/24:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002636)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/22:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002637)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/22:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002638)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002639)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002643)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0002647)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002648)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002649)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002650)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002651)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/25:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002652)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/25:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002653)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002654)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/23:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002655)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/23:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002656)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002657)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(9Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002660)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002661)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002663)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/22:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002664)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/22:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002665)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/22:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002666)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002667)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002669)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002670)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/26:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002677)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(10:0/26:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002678)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/24:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002679)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/24:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002680)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(12:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002681)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002682)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:0/22:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0002683)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(11Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0002685)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0002689)
- Molybdenum Cofactor Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012017)
- Flavonoid Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012021)
- Flavone and Flavonol Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012025)
- Choline Biosynthesis I (PathBank: SMP0012026)
- Choline Biosynthesis II (PathBank: SMP0012027)
- Phylloquinol Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012040)
- Plastoquinol-9 Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012043)
- Thio-Molybdenum Cofactor Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0012046)
- Glycine Betaine Biosynthesis I (PathBank: SMP0012047)
- Glycine Betaine Biosynthesis II (PathBank: SMP0012048)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(14:1(9Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014245)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014274)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(15:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014275)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014303)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014304)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014305)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014332)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014333)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014334)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(16:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014335)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014361)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014362)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014363)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014364)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014365)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014390)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014391)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014392)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014393)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014394)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014395)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014419)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014420)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014421)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014422)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014423)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014424)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014447)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014448)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014449)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014450)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014451)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014452)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014453)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014454)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014476)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014477)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014478)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014479)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014480)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014481)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014482)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014483)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014484)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014505)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014506)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014507)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014508)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014509)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014510)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014511)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014512)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014513)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014514)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014534)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014535)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014536)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014537)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014538)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014539)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014540)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014541)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014542)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014543)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014544)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014563)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014564)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014565)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014566)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014567)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014568)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014569)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014570)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014571)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014572)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014573)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014574)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014592)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014593)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014594)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014595)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014596)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014597)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014598)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014599)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014600)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014601)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014602)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014603)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014604)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014621)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014622)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014623)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014624)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014625)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014626)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014627)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014628)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014629)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014630)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014631)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014632)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014633)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014634)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014650)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014651)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014652)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014653)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014654)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014655)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014656)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014657)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014658)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014659)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014660)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014661)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014662)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014663)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014664)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014679)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014680)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014681)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014682)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014683)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014684)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014685)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014686)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014687)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014688)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014689)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014690)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014691)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014692)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014693)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014694)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014708)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014709)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014710)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014711)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014712)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014713)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014714)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014715)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014716)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014717)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014718)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014719)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014720)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014721)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014722)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014723)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014724)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014737)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014738)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014739)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014740)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014741)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014742)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014743)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014744)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014745)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014746)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014747)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014748)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014749)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014750)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014751)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014752)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014753)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014754)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014766)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014767)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014768)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014769)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014770)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014771)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014772)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014773)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014774)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014775)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014776)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014777)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014778)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014779)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014780)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014781)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014782)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014783)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014784)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014795)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014796)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014797)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014798)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014799)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014800)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014801)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014802)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014803)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014804)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014805)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014806)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014807)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014808)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014809)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014810)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014811)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014812)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014813)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014814)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014824)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014825)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014826)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014827)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014828)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014829)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014830)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014831)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014832)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014833)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014834)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014835)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014836)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014837)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014838)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014839)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014840)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014841)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014842)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014843)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:1(13Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014844)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014853)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014854)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014855)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014856)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014857)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014858)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014859)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014860)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014861)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014862)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014863)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014864)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014865)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014866)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014867)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014868)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014869)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014870)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014871)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014872)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014873)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:2(13Z,16Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014874)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014882)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014883)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014884)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014885)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014886)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014887)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014888)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014889)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014890)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014891)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014892)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014893)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014894)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014895)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014896)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014897)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014898)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014899)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014900)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014901)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014902)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014903)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014904)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014911)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014912)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014913)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014914)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014915)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014916)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014917)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014918)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014919)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014920)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014921)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014922)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014923)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014924)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014925)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014926)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014927)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014928)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014929)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014930)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014931)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014932)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014933)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014934)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014940)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014941)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014942)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014943)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014944)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014945)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014946)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014947)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014948)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014949)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014950)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014951)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014952)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014953)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014954)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014955)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014956)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014957)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014958)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014959)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014960)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014961)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014962)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014963)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014964)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014969)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014970)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0014971)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0014972)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014973)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0014974)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014975)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014976)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014977)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014978)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014979)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014980)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0014981)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014982)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014983)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014984)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014985)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014986)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014987)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014988)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0014989)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014990)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014991)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014992)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014993)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014994)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0014998)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0014999)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0015000)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0015001)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015002)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0015003)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015004)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015005)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015006)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015007)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015008)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015009)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0015010)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015011)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015012)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015013)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015014)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015015)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015016)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015017)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0015018)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015019)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015020)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015021)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015022)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015023)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:0/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015024)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/14:0) (PathBank: SMP0015027)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/14:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015028)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/15:0) (PathBank: SMP0015029)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/16:0) (PathBank: SMP0015030)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/16:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015031)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:0) (PathBank: SMP0015032)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015033)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:1(9Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015034)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015035)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015036)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015037)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015038)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:0) (PathBank: SMP0015039)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:1(11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015040)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:2(11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015041)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:3(5Z,8Z,11Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015042)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:3(8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015043)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015044)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015045)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015046)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0015047)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015048)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:2(13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015049)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:4(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015050)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015051)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:5(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015052)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)) (PathBank: SMP0015053)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(24:1(15Z)/24:0) (PathBank: SMP0015054)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030241)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030242)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030243)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030244)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030245)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030246)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030247)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030248)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D3/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030249)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030250)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030251)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030252)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030253)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030254)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030255)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030256)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030257)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11D5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030258)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030259)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030260)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030261)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030262)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030263)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030264)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030265)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030266)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13D5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030267)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030268)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030269)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030270)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030271)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030272)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030273)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030274)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030275)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D3/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030276)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030277)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030278)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030279)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030280)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030281)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030282)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030283)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030284)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9D5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030285)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030286)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030287)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030288)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030289)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030290)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030291)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030292)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030293)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M3/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030294)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030295)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030296)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030297)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030298)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030299)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030300)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030301)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030302)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(11M5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030303)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030304)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030305)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030306)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030307)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030308)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030309)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030310)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030311)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(13M5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030312)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11D3) (PathBank: SMP0030313)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11D5) (PathBank: SMP0030314)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/13D5) (PathBank: SMP0030315)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/9D3) (PathBank: SMP0030316)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/9D5) (PathBank: SMP0030317)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11M3) (PathBank: SMP0030318)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/11M5) (PathBank: SMP0030319)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/13M5) (PathBank: SMP0030320)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(9M5/9M5) (PathBank: SMP0030321)
- Stilbenoid, Diarylheptanoid, and Gingerol Biosynthesis (PathBank: SMP0063461)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063838)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(9Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063848)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063857)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063865)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063872)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063878)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:0/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063883)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(11Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063887)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(13Z)/20:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063890)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(13Z)/22:0) (PathBank: SMP0063891)
- Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis PC(20:1(13Z)/22:1(13Z)) (PathBank: SMP0063892)
- Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Metabolism (PathBank: SMP0070041)
- Juvenile Hormone Synthesis (PathBank: SMP0121063)
- Arsenate Detoxification (PathBank: SMP0121123)
Disease pathwayDrug action pathwaySignaling pathwayProtein pathway |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | 78 °C | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 1.19 g/l | ALOGPS | | LogP | -5.3 | ChemAxon |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| S-Adenosylmethionine,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3480.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3561.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3574.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,1TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3584.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,1TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3633.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3430.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3568.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3576.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3534.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3431.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3449.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3487.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3459.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3471.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3539.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3471.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3544.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3385.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3476.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3498.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3514.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #13 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3461.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #14 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3500.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #15 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3514.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #16 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3465.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #17 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3602.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #18 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3493.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3390.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3458.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3395.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3458.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3473.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3512.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3435.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3390.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3337.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3364.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4964.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3418.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3478.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4581.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3450.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3471.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4849.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3452.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3479.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5054.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #13 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3428.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #13 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3445.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #13 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4949.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #14 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3553.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #14 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3564.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #14 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4944.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #15 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3449.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #15 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3500.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #15 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4605.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #16 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3553.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #16 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3555.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #16 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4917.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #17 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3453.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #17 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3494.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #17 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4576.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #18 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3583.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #18 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3603.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #18 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4731.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3438.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3390.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5066.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3443.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3453.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4807.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3494.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3465.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 5054.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3425.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3430.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4811.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3442.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3447.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4778.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3498.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3458.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 5037.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3427.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3425.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4791.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3580.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3535.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4952.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3425.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3459.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4481.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3432.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3475.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4272.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3567.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3582.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4381.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3566.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3575.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4353.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3483.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3451.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4821.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3427.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3395.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4560.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3571.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3541.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4590.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3412.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3458.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4231.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3569.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3533.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4563.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3414.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3456.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4199.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3584.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3560.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4380.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3529.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3557.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,5TMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4600.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3569.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3533.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4325.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3432.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3433.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3939.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3592.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3533.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4053.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3591.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3529.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4022.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3559.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 3546.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,6TMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 4067.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3743.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3796.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3801.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,1TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3813.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,1TBDMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3849.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3885.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3958.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4005.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3918.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3886.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3870.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3883.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3904.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3911.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3930.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3909.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,2TBDMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3923.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3992.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4017.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4025.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4128.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #13 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4022.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #14 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4024.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #15 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4128.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #16 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4021.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #17 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4156.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #18 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4034.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3966.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 3999.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3968.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3993.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4002.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4100.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 3983.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,3TBDMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3989.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4065.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4025.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4983.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4095.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4192.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #10 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4613.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4130.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4157.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #11 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4850.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4219.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4109.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #12 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5034.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #13 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4138.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #13 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4136.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #13 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4918.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #14 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4265.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #14 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4238.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #14 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4889.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #15 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4153.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #15 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4205.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #15 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4641.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #16 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4265.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #16 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4226.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #16 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4871.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #17 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4148.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #17 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4194.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #17 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4619.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #18 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4304.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #18 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4288.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #18 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4703.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4115.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4085.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5035.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4100.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4161.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4817.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4208.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4127.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 5031.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4106.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4141.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #5 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 4829.1 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4096.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4150.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #6 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4797.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4211.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4115.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #7 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 5015.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4104.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4131.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #8 | C[S+](CC[C@H](N)C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 4811.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4233.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4228.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | S-Adenosylmethionine,4TBDMS,isomer #9 | C[S+](CC[C@@H](C(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C[C@H]1O[C@@H](N2C=NC3=C(N[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)N=CN=C32)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 4890.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0a5c-5965000000-324e4a3cbf936132bcf1 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine GC-MS (3 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00ea-7958582000-3dd40cf273f182ee53dd | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-0002-0019000000-6dfa0dc65a9863755c2a | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-0udj-0293000000-57cc9d4430592060d41d | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-0udr-1940000000-ed4985bea80649d27efe | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-000b-8920000000-8f05e9898f0d26ddf3f8 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-000e-9400000000-e5c5617045d9915e8e46 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine LC-ESI-IT , positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0090000000-93017671648813ece8a5 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-0914000000-95030ceaf1c187dcf656 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-0900000000-c3fae8b7a68475b614a4 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-2900000000-44078fd7eaeafcc5bba8 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-1927000000-02f9d1735282c46e7318 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-1900000000-aa88bbdd6c68c8e33363 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - S-Adenosylmethionine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0bti-7900000000-003aba988a5c7e2f6534 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Mitochondria
- Nucleus
- Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Feces
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Epidermis
- Eye Lens
- Fibroblasts
- Intestine
- Kidney
- Neuron
- Ovary
- Placenta
- Prostate
- Skeletal Muscle
- Testis
|
|---|
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0550-0.116 uM | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.127-0.259 uM | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.25 (0.14 - 0.38) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details |
|
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.11 (0.087-0.17) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Neurodegenerative diseases | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.496 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Female | Adenosine kinase deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.677 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Adenosine kinase deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.264 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Adenosine kinase deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.291 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Female | Adenosine kinase deficiency | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Enthesitis-related arthritis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 28.4 (25.3-31.6) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Diabetes | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Neurodegenerative disease |
|---|
- Obeid R, Kostopoulos P, Knapp JP, Kasoha M, Becker G, Fassbender K, Herrmann W: Biomarkers of folate and vitamin B12 are related in blood and cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem. 2007 Feb;53(2):326-33. Epub 2007 Jan 2. [PubMed:17200133 ]
| | Adenosine kinase deficiency |
|---|
- Bjursell MK, Blom HJ, Cayuela JA, Engvall ML, Lesko N, Balasubramaniam S, Brandberg G, Halldin M, Falkenberg M, Jakobs C, Smith D, Struys E, von Dobeln U, Gustafsson CM, Lundeberg J, Wedell A: Adenosine kinase deficiency disrupts the methionine cycle and causes hypermethioninemia, encephalopathy, and abnormal liver function. Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Oct 7;89(4):507-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.09.004. Epub 2011 Sep 28. [PubMed:21963049 ]
| | Diabetes mellitus type 2 |
|---|
- Hoppel CL, Genuth SM: Urinary excretion of acetylcarnitine during human diabetic and fasting ketosis. Am J Physiol. 1982 Aug;243(2):E168-72. [PubMed:6810706 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 614300 (Adenosine kinase deficiency)
- 125853 (Diabetes mellitus type 2)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB031152 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00007347 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 21169292 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00019 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | S-ADENOSYLMETHIONINE |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 33530 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | S-Adenosyl_methionine |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 6064 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 34756 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 15414 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | AMET |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Lin, Jian-Ping; Tian, Jun; You, Jian-Feng; Jin, Zhi-Hua; Xu, Zhi-Nan; Cen, Pei-Lin. An effective strategy for the co-production of S-adenosyl-L-methionine and glutathione by fed-batch fermentation. Biochemical Engineering Journal (2004), 21(1), 19-25. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Chamberlin ME, Ubagai T, Mudd SH, Wilson WG, Leonard JV, Chou JY: Demyelination of the brain is associated with methionine adenosyltransferase I/III deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1996 Aug 15;98(4):1021-7. [PubMed:8770875 ]
- Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. doi: 10.1038/nature07762. [PubMed:19212411 ]
- Hoppel CL, Genuth SM: Urinary excretion of acetylcarnitine during human diabetic and fasting ketosis. Am J Physiol. 1982 Aug;243(2):E168-72. [PubMed:6810706 ]
- Koeberl DD, Young SP, Gregersen NS, Vockley J, Smith WE, Benjamin DK Jr, An Y, Weavil SD, Chaing SH, Bali D, McDonald MT, Kishnani PS, Chen YT, Millington DS: Rare disorders of metabolism with elevated butyryl- and isobutyryl-carnitine detected by tandem mass spectrometry newborn screening. Pediatr Res. 2003 Aug;54(2):219-23. Epub 2003 May 7. [PubMed:12736383 ]
- Struys EA, Jansen EE, de Meer K, Jakobs C: Determination of S-adenosylmethionine and S-adenosylhomocysteine in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid by stable-isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2000 Oct;46(10):1650-6. [PubMed:11017945 ]
- Scalabrino G, Pigatto P, Ferioli ME, Modena D, Puerari M, Caru A: Levels of activity of the polyamine biosynthetic decarboxylases as indicators of degree of malignancy of human cutaneous epitheliomas. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Mar;74(3):122-4. [PubMed:7359002 ]
- Kaneoka H, Uesugi N, Moriguchi A, Hirose S, Takayanagi M, Yamaguchi S, Shigematsu Y, Yasuno T, Sasatomi Y, Saito T: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase II deficiency due to a novel gene variant in a patient with rhabdomyolysis and ARF. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005 Mar;45(3):596-602. [PubMed:15754283 ]
- Rosen RT, Hiserodt RD, Fukuda EK, Ruiz RJ, Zhou Z, Lech J, Rosen SL, Hartman TG: The determination of metabolites of garlic preparations in breath and human plasma. Biofactors. 2000;13(1-4):241-9. [PubMed:11237188 ]
- McFadden PN, Horwitz J, Clarke S: Protein carboxyl methyltransferase from cow eye lens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 15;113(2):418-24. [PubMed:6870865 ]
- Garibotto G, Sofia A, Valli A, Tarroni A, Di Martino M, Cappelli V, Aloisi F, Procopio V: Causes of hyperhomocysteinemia in patients with chronic kidney diseases. Semin Nephrol. 2006 Jan;26(1):3-7. [PubMed:16412817 ]
- Spiekerkoetter U, Tokunaga C, Wendel U, Mayatepek E, Ijlst L, Vaz FM, van Vlies N, Overmars H, Duran M, Wijburg FA, Wanders RJ, Strauss AW: Tissue carnitine homeostasis in very-long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase-deficient mice. Pediatr Res. 2005 Jun;57(6):760-4. Epub 2005 Mar 17. [PubMed:15774826 ]
- Jones MG, Goodwin CS, Amjad S, Chalmers RA: Plasma and urinary carnitine and acylcarnitines in chronic fatigue syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. 2005 Oct;360(1-2):173-7. [PubMed:15967423 ]
- Kelm A, Shaw L, Schauer R, Reuter G: The biosynthesis of 8-O-methylated sialic acids in the starfish Asterias rubens--isolation and characterisation of S-adenosyl-L-methionine:sialate-8-O-methyltransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1998 Feb 1;251(3):874-84. [PubMed:9490063 ]
- Solano AR, Sanchez ML, Podesta EJ, Turyn D, Dellacha JM: Membrane methylation in isolated rat testis interstitial cells unmasks functional luteinizing hormone receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 2;928(1):107-13. [PubMed:3828399 ]
- D'Erme M, Santoro R, Allegra P, Reale A, Marenzi S, Strom R, Caiafa P: Inhibition of CpG methylation in linker DNA by H1 histone. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 May 28;1173(2):209-16. [PubMed:8504169 ]
- Scott JM, Weir DG: The methyl folate trap. A physiological response in man to prevent methyl group deficiency in kwashiorkor (methionine deficiency) and an explanation for folic-acid induced exacerbation of subacute combined degeneration in pernicious anaemia. Lancet. 1981 Aug 15;2(8242):337-40. [PubMed:6115113 ]
| Show more...
|---|