| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-09-22 17:43:42 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000363 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone |
|---|
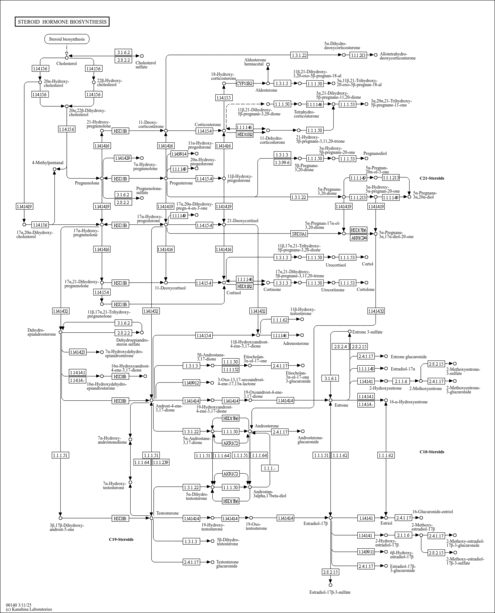
| Description | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone is a 21-carbon steroid that is converted from pregnenolone by cytochrome P450 17alpha hydroxylase/C17,20 lyase (CYP17, EC 1.14.99.9). 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone is an intermediate in the delta-5 pathway of biosynthesis of gonadal steroid hormones and the adrenal corticosteroids. The first, rate-limiting and hormonally regulated step in the biosynthesis of all steroid hormones is the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone. The conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone is accomplished by the cleavage of the cholesterol side chain, catalyzed by a mitochondrial cytochrome P450 enzyme termed P450scc where scc designates Side Chain Cleavage. All steroid hormones are made from the pregnenolone produced by P450scc; thus, the presence or absence of each of the activities of CYP17 directs this pregnenolone towards its final metabolic pathway. While all cytochrome P450 enzymes can catalyze multiple reactions on a single active site, CYP17 is the only one described to date in which these multiple activities are differentially regulated by a physiologic process. 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone is converted to dehydroepiandrosterone by the 17,20 lyase activity of CYP17. The ratio of the 17,20 lyase to 17 alpha-hydroxylase activity of CYP17 determines the ratio of C21 to C19 steroids produced. This ratio is regulated post-translationally by at least three factors: the abundance of the electron-donating protein P450 oxidoreductase, the presence of cytochrome b5, and the serine phosphorylation of CYP17. (PMID: 12573809 ). |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C21H32O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 332.477 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 332.23514489 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | Not Available |
|---|
| Traditional Name | Not Available |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 387-79-1 |
|---|
| SMILES | Not Available |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C21H32O3/c1-13(22)21(24)11-8-18-16-5-4-14-12-15(23)6-9-19(14,2)17(16)7-10-20(18,21)3/h4,15-18,23-24H,5-12H2,1-3H3/t15-,16+,17-,18-,19-,20-,21-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | JERGUCIJOXJXHF-TVWVXWENSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Classification | Not classified |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 266 - 271 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,1TMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 2934.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,1TMS,isomer #2 | CC(=O)[C@@]1(O)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 2913.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,1TMS,isomer #3 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 2827.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,2TMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 2961.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,2TMS,isomer #2 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 2958.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,2TMS,isomer #3 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 2855.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,3TMS,isomer #1 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 2964.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,3TMS,isomer #1 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 2904.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,3TMS,isomer #1 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 3228.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 3183.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(=O)[C@@]1(O)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 3170.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 3115.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 3457.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 3503.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 3385.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 3724.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 3605.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | 17a-Hydroxypregnenolone,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | C=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@]1(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@H]2[C@@H]3CC=C4C[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)CC[C@]4(C)[C@H]3CC[C@@]21C | 3481.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Membrane (predicted from logP)
- Endoplasmic reticulum
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | |
|---|
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00180-0.00451 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00211-0.0256 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00902 +/- 0.00361 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.000300-0.0240 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.000782 +/- 0.000993 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00656 +/- 0.00562 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.003 (0.000 - 0.006) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.006 (0.001-0.012) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.000271 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Female | Adrenal insufficiency, congenital, with 46,XY sex reversal, partial or complete | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00123 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Female | Adrenal insufficiency, congenital, with 46,XY sex reversal, partial or complete | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0126 +/- 0.0105 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Not Specified | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00440 +/- 0.00280 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.159 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.741 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Male | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0264-0.103 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0843-1.262 uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00230 +/- 0.00200 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00300 +/- 0.00250 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00380 +/- 0.00210 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00896 +/- 0.00770 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0186 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0120-0.180 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Antley-Bixler syndrome with genital anomalies and disordered steroidogenesis | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.136 +/- 0.129 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.00439 +/- 0.00896 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.176 +/- 0.186 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.0111 +/- 0.0219 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Not Specified | Cancer patients undergoing total body irradiation | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency |
|---|
- Hattori N, Ishihara T, Moridera K, Hino M, Ikekubo K, Kurahachi H: A case of late-onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to partial 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency. Endocr J. 1993 Feb;40(1):107-9. [PubMed:7951484 ]
- Lutfallah C, Wang W, Mason JI, Chang YT, Haider A, Rich B, Castro-Magana M, Copeland KC, David R, Pang S: Newly proposed hormonal criteria via genotypic proof for type II 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Jun;87(6):2611-22. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.6.8615. [PubMed:12050224 ]
- Benkert AR, Young M, Robinson D, Hendrickson C, Lee PA, Strauss KA: Severe Salt-Losing 3beta-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Deficiency: Treatment and Outcomes of HSD3B2 c.35G>A Homozygotes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Aug;100(8):E1105-15. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-2098. Epub 2015 Jun 16. [PubMed:26079780 ]
| | Antley-Bixler syndrome with genital anomalies and disordered steroidogenesis |
|---|
- Fukami M, Hasegawa T, Horikawa R, Ohashi T, Nishimura G, Homma K, Ogata T: Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency in three patients initially regarded as having 21-hydroxylase deficiency and/or aromatase deficiency: diagnostic value of urine steroid hormone analysis. Pediatr Res. 2006 Feb;59(2):276-80. doi: 10.1203/01.pdr.0000195825.31504.28. [PubMed:16439592 ]
| | Adrenal insufficiency, congenital, with 46,XY sex reversal, partial or complete |
|---|
- Kim CJ, Lin L, Huang N, Quigley CA, AvRuskin TW, Achermann JC, Miller WL: Severe combined adrenal and gonadal deficiency caused by novel mutations in the cholesterol side chain cleavage enzyme, P450scc. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Mar;93(3):696-702. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-2330. Epub 2008 Jan 8. [PubMed:18182448 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 201810 (Adrenal hyperplasia, congenital, due to 3-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency)
- 201750 (Antley-Bixler syndrome with genital anomalies and disordered steroidogenesis)
- 613743 (Adrenal insufficiency, congenital, with 46,XY sex reversal, partial or complete)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| External Links | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Kaspar, Emanuel; Hiersemann, Wolfgang; Schenck, Martin. Preparation from their esters of steroid alcohols that are sensitive to acids and alkali. (1958), DE 1028572 19580424 CAN 54:74845 AN 1960:74845 CAPLUS |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Shimozawa K, Saisho S, Yata J, Kambegawa A: Age-related changes in serum 17-hydroxypregnenolone and 17-hydroxypregnenolone sulfate concentrations in human infancy and childhood. Endocrinol Jpn. 1988 Apr;35(2):189-95. [PubMed:3208699 ]
- Rodriguez-Rigau LJ, Weiss DB, Smith KD, Steinberger E: Suggestion of abnormal testicular steroidogenesis in some oligospermic men. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1978 Feb;87(2):400-12. [PubMed:580138 ]
- Kaufman FR, Costin G, Goebelsmann U, Stanczyk FZ, Zachmann M: Male pseudohermaphroditism due to 17,20-desmolase deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Jul;57(1):32-6. [PubMed:6853680 ]
- Miller WL: Androgen biosynthesis from cholesterol to DHEA. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002 Dec 30;198(1-2):7-14. [PubMed:12573809 ]
|
|---|