| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2025-05-29 18:10:14 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000271 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Sarcosine |
|---|
| Description | Sarcosine is the N-methyl derivative of glycine. Sarcosine is metabolized to glycine by the enzyme sarcosine dehydrogenase, while glycine-N-methyl transferase generates sarcosine from glycine. Sarcosine is a natural amino acid found in muscles and other body tissues. In the laboratory it may be synthesized from chloroacetic acid and methylamine. Sarcosine is naturally found in the metabolism of choline to glycine. Sarcosine is sweet to the taste and dissolves in water. It is used in manufacturing biodegradable surfactants and toothpastes as well as in other applications. Sarcosine is ubiquitous in biological materials and is present in such foods as egg yolks, turkey, ham, vegetables, legumes, etc. Sarcosine is formed from dietary intake of choline and from the metabolism of methionine, and is rapidly degraded to glycine. Sarcosine has no known toxicity, as evidenced by the lack of phenotypic manifestations of sarcosinemia, an inborn error of sarcosine metabolism. Sarcosinemia can result from severe folate deficiency because of the folate requirement for the conversion of sarcosine to glycine (Wikipedia ). Sarcosine has recently been identified as a biomarker for invasive prostate cancer. It was found to be greatly increased during prostate cancer progression to metastasis and could be detected in urine. Sarcosine levels were also increased in invasive prostate cancer cell lines relative to benign prostate epithelial cells (PMID: 19212411 ). |
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C3H7NO2/c1-4-2-3(5)6/h4H,2H2,1H3,(H,5,6) |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (Methylamino)acetic acid | ChEBI | | (Methylamino)ethanoic acid | ChEBI | | L-Sarcosine | ChEBI | | MeGly | ChEBI | | Methylaminoacetic acid | ChEBI | | N-Methylaminoacetic acid | ChEBI | | N-Methylglycine | ChEBI | | Sar | ChEBI | | Sarcosinic acid | ChEBI | | (Methylamino)acetate | Generator | | (Methylamino)ethanoate | Generator | | Methylaminoacetate | Generator | | N-Methylaminoacetate | Generator | | Sarcosinate | Generator | | (Methylamino)-acetate | HMDB | | (Methylamino)-acetic acid | HMDB | | Methylglycine | HMDB | | N-Methyl-glycine | HMDB | | Sarcosin | HMDB | | Sodium sarcosinate | HMDB | | Magnesium sarcosylate | HMDB | | Sarcosinate, sodium | HMDB | | Sarcosine hydrochloride | HMDB | | Sarcosylate, magnesium | HMDB | | N Methylglycine | HMDB | | Sarcosine monosodium salt | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C3H7NO2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 89.0932 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 89.047678473 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-(methylamino)acetic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | sarcosine |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 107-97-1 |
|---|
| SMILES | CNCC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C3H7NO2/c1-4-2-3(5)6/h4H,2H2,1H3,(H,5,6) |
|---|
| InChI Key | FSYKKLYZXJSNPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha amino acids. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alpha amino acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-amino acid
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Secondary aliphatic amine
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Secondary amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 208 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 300 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | -2.78 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Sarcosine,1TMS,isomer #1 | CNCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C | 964.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Sarcosine,1TMS,isomer #2 | CN(CC(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1128.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Sarcosine,2TMS,isomer #1 | CN(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1164.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Sarcosine,2TMS,isomer #1 | CN(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1132.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Sarcosine,2TMS,isomer #1 | CN(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1211.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Sarcosine,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CNCC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1187.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Sarcosine,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CN(CC(=O)O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1358.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Sarcosine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CN(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1599.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Sarcosine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CN(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1569.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Sarcosine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CN(CC(=O)O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 1517.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014i-0900000000-3703e9255c5a3d53576e | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (2 TMS) | splash10-00xr-9800000000-b066cf015be7d1b1ec05 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-MS (2 TMS) | splash10-014i-0900000000-73acbf4b13dbcd53efe1 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014i-0900000000-22864bae97055c3845b6 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014i-0900000000-3703e9255c5a3d53576e | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00xr-9800000000-b066cf015be7d1b1ec05 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014i-0900000000-73acbf4b13dbcd53efe1 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-014i-0900000000-9559630483fd184becb6 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-7a4141479c88d11af74a | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-847886894070391d8fdd | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Sarcosine GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0006-9000000000-335905bb8c6b7e52ff70 | 2014-09-20 | Not Available | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0006-9000000000-da0fd904589ef164065a | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0006-9000000000-6b30a9c471d171cacad9 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0006-9000000000-851a04dbd34e75febf9d | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-86301ee1b7f5d158901e | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-32b1ca1874d0fcb3f9c7 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-37db595fcf7364600bc9 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-0b3e92ad374e013024ea | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-ef853c67634f1a7da8f5 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-63e1ee6f897ea7a61e52 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-bab0ab3587973d3ad4aa | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-d017a51a9abbbcf31dce | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-86301ee1b7f5d158901e | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-645df370acbb7cac5322 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-37db595fcf7364600bc9 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-0b3e92ad374e013024ea | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-ef853c67634f1a7da8f5 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-5701e8afc0a34aa34653 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-bab0ab3587973d3ad4aa | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-d017a51a9abbbcf31dce | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-5fd27462e0d106e4c5a6 | 2015-04-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-4f822ba462b1fbffce17 | 2015-04-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0006-9000000000-4125b1890cbe03ae7283 | 2015-04-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-c7e62ee2909dfb0a067c | 2015-04-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-000i-9000000000-8d4f2d4c6d399cbf0c9f | 2015-04-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Sarcosine 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-052f-9000000000-c8a4e61d51664ed38b96 | 2015-04-25 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2021-10-10 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Extracellular
- Mitochondria
- Peroxisome
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Feces
- Saliva
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | |
|---|
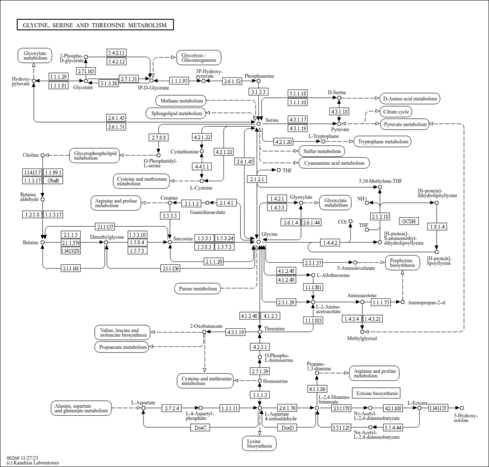
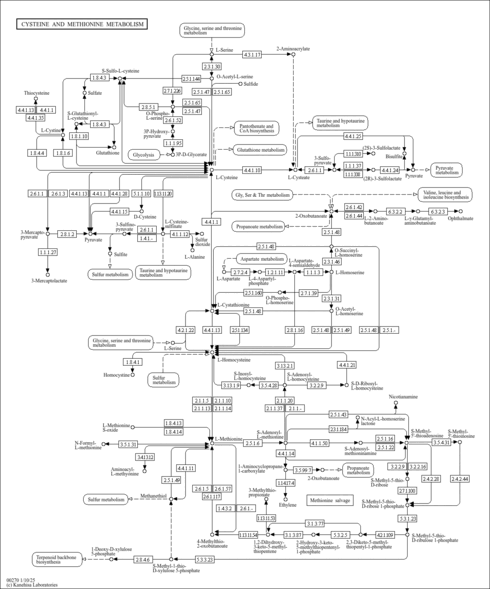
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.77 ± 0.66 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | <10 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | <0.001 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.4 +/- 0.6 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.01 ± 0.24 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.23 ± 0.4 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.42 ± 0.79 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.91 ± 0.45 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1 ± 0.51 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.13 ± 0.42 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 5.25 ± 1.53 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.13 ± 0.36 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | >10 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 3.48 +/- 2.23 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 2.53 +/- 1.74 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 4.15 +/- 2.02 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 10.42 +/- 4.19 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.9 (0.5-5.4) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.6 (0.2-9.4) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.47 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 3.69 (2.01-5.49) umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <1.36 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <0.34 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <0.34 umol/mmol creatinine | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <0.23 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <1.018 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <50 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <8.48 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.28(0.51-4.79) umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.74(0.77-11.36) umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.55-9.98 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 5-25 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 5.946 +/- 10.638 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.24-0.34 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.25-0.31 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.35 +/- 1.21 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <0.00100 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <1.467 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <1.467 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <56.5 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 300.0 (80.0-603.0) uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Sarcosinemia | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Dimethylglycinuria | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 238-379 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Sarcosinemia | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | gastric cancer | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 654.1 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Female | Sarcosinemia | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 200-300 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Female | Sarcosinemia | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 7-12 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Sarcosinemia | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 5-17 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | Sarcosinemia | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 3.37 +/- 1.84 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Alzheimer's disease | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 4.84 +/- 3.39 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Lewy body disease | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 20.53 +/- 27.29 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Frontotemporal lobe dementia | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Prostate cancer | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 12.028 +/- 27.256 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Eosinophilic esophagitis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 361.333 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Female | Sarcosinemia | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2703.95 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Female | Sarcosinemia | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 631-1214 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Sarcosinemia | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Dimethylglycinuria | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Bladder cancer | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Sarcosinemia |
|---|
- Levy HL, Coulombe JT, Benjamin R: Massachusetts Metabolic Disorders Screening Program: III. Sarcosinemia. Pediatrics. 1984 Oct;74(4):509-13. [PubMed:6207480 ]
- Sewell AC, Krille M, Wilhelm I: Sarcosinaemia in a retarded, amaurotic child. Eur J Pediatr. 1986 Feb;144(5):508-10. [PubMed:2420598 ]
- Meissner T, Mayatepek E: Sarcosinaemia in a patient with severe progressive neurological damage and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1997 Sep;20(5):717-8. [PubMed:9323574 ]
- Benarrosh A, Garnotel R, Henry A, Arndt C, Gillery P, Motte J, Bakchine S: A young adult with sarcosinemia. No benefit from long duration treatment with memantine. JIMD Rep. 2013;9:93-96. doi: 10.1007/8904_2012_185. Epub 2012 Oct 21. [PubMed:23430553 ]
- G.Frauendienst-Egger, Friedrich K. Trefz (2017). MetaGene: Metabolic & Genetic Information Center (MIC: http://www.metagene.de). METAGENE consortium.
- Ronald Scott CC. (2014). In: Valle D, Beaudet AL, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW, Antonarakis SE, Ballabio A, Gibson K, Mitchell G. eds. The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease New York, NY. McGraw-Hill.
| | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Ritchie SA, Ahiahonu PW, Jayasinghe D, Heath D, Liu J, Lu Y, Jin W, Kavianpour A, Yamazaki Y, Khan AM, Hossain M, Su-Myat KK, Wood PL, Krenitsky K, Takemasa I, Miyake M, Sekimoto M, Monden M, Matsubara H, Nomura F, Goodenowe DB: Reduced levels of hydroxylated, polyunsaturated ultra long-chain fatty acids in the serum of colorectal cancer patients: implications for early screening and detection. BMC Med. 2010 Feb 15;8:13. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-8-13. [PubMed:20156336 ]
- Goedert JJ, Sampson JN, Moore SC, Xiao Q, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Ahn J, Shi J, Sinha R: Fecal metabolomics: assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2089-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu131. Epub 2014 Jul 18. [PubMed:25037050 ]
| | Stomach cancer |
|---|
- Song H, Peng JS, Dong-Sheng Y, Yang ZL, Liu HL, Zeng YK, Shi XP, Lu BY: Serum metabolic profiling of human gastric cancer based on gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012 Jan;45(1):78-85. Epub 2011 Nov 25. [PubMed:22124703 ]
| | Alzheimer's disease |
|---|
- Tsuruoka M, Hara J, Hirayama A, Sugimoto M, Soga T, Shankle WR, Tomita M: Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry-based metabolome analysis of serum and saliva from neurodegenerative dementia patients. Electrophoresis. 2013 Oct;34(19):2865-72. doi: 10.1002/elps.201300019. Epub 2013 Sep 6. [PubMed:23857558 ]
| | Frontotemporal dementia |
|---|
- Tsuruoka M, Hara J, Hirayama A, Sugimoto M, Soga T, Shankle WR, Tomita M: Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry-based metabolome analysis of serum and saliva from neurodegenerative dementia patients. Electrophoresis. 2013 Oct;34(19):2865-72. doi: 10.1002/elps.201300019. Epub 2013 Sep 6. [PubMed:23857558 ]
| | Lewy body disease |
|---|
- Tsuruoka M, Hara J, Hirayama A, Sugimoto M, Soga T, Shankle WR, Tomita M: Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry-based metabolome analysis of serum and saliva from neurodegenerative dementia patients. Electrophoresis. 2013 Oct;34(19):2865-72. doi: 10.1002/elps.201300019. Epub 2013 Sep 6. [PubMed:23857558 ]
| | Eosinophilic esophagitis |
|---|
- Slae, M., Huynh, H., Wishart, D.S. (2014). Analysis of 30 normal pediatric urine samples via NMR spectroscopy (unpublished work). NA.
| | Prostate cancer |
|---|
- Soliman LC, Hui Y, Hewavitharana AK, Chen DD: Monitoring potential prostate cancer biomarkers in urine by capillary electrophoresis-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2012 Dec 7;1267:162-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.07.021. Epub 2012 Jul 14. [PubMed:22824219 ]
| | Dimethylglycine Dehydrogenase Deficiency |
|---|
- Moolenaar SH, Poggi-Bach J, Engelke UF, Corstiaensen JM, Heerschap A, de Jong JG, Binzak BA, Vockley J, Wevers RA: Defect in dimethylglycine dehydrogenase, a new inborn error of metabolism: NMR spectroscopy study. Clin Chem. 1999 Apr;45(4):459-64. [PubMed:10102904 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 268900 (Sarcosinemia)
- 114500 (Colorectal cancer)
- 137215 (Stomach cancer)
- 104300 (Alzheimer's disease)
- 600274 (Frontotemporal dementia)
- 610247 (Eosinophilic esophagitis)
- 176807 (Prostate cancer)
- 605850 (Dimethylglycine Dehydrogenase Deficiency)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB12519 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB004048 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 1057 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00213 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | SARCOSINE |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 34275 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Sarcosine |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 51 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 1088 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 15611 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | SARCS |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000130 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Cipens, G.; Slavinska, V.; Sile, D.; Kreile, D.; Strautina, A.; Krikis, A.; Gutmanis, A. Synthesis of sarcosine and its use. Latvijas PSR Zinatnu Akademijas Vestis, Kimijas Serija (1986), (5), 515-24. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Download (PDF) |
|---|
| General References | - Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. doi: 10.1038/nature07762. [PubMed:19212411 ]
- Shoemaker JD, Elliott WH: Automated screening of urine samples for carbohydrates, organic and amino acids after treatment with urease. J Chromatogr. 1991 Jan 2;562(1-2):125-38. [PubMed:2026685 ]
- Boulat O, Gradwohl M, Matos V, Guignard JP, Bachmann C: Organic acids in the second morning urine in a healthy Swiss paediatric population. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2003 Dec;41(12):1642-58. [PubMed:14708889 ]
- Silwood CJ, Lynch E, Claxson AW, Grootveld MC: 1H and (13)C NMR spectroscopic analysis of human saliva. J Dent Res. 2002 Jun;81(6):422-7. [PubMed:12097436 ]
- Akare S, Martinez JD: Bile acid induces hydrophobicity-dependent membrane alterations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Jun 15;1735(1):59-67. [PubMed:15951237 ]
- Lim DS, Roberts R, Marian AJ: Expression profiling of cardiac genes in human hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: insight into the pathogenesis of phenotypes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001 Oct;38(4):1175-80. [PubMed:11583900 ]
- Bales JR, Sadler PJ, Nicholson JK, Timbrell JA: Urinary excretion of acetaminophen and its metabolites as studied by proton NMR spectroscopy. Clin Chem. 1984 Oct;30(10):1631-6. [PubMed:6206966 ]
- Heil M, Podebrad F, Prado E, Beck T, Mosand A, Sewell AC, Bohles H, Lehnert W: Enantioselective analysis of ketone bodies in patients with beta-ketothiolase deficiency, medium-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency and ketonemic vomiting. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2000 Mar 10;739(2):313-24. [PubMed:10755375 ]
- Kang ES, Seyer J, Todd TA, Herrera C: Variability in the phenotypic expression of abnormal sarcosine metabolism in a family. Hum Genet. 1983;64(1):80-5. [PubMed:6192074 ]
- Vallera DA, Todhunter DA, Kuroki DW, Shu Y, Sicheneder A, Chen H: A bispecific recombinant immunotoxin, DT2219, targeting human CD19 and CD22 receptors in a mouse xenograft model of B-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005 May 15;11(10):3879-88. [PubMed:15897589 ]
- Hitomi J, Yamaguchi K, Kikuchi Y, Kimura T, Maruyama K, Nagasaki K: A novel calcium-binding protein in amniotic fluid, CAAF1: its molecular cloning and tissue distribution. J Cell Sci. 1996 Apr;109 ( Pt 4):805-15. [PubMed:8718672 ]
| Show more...
|---|