| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-05-30 20:55:50 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000259 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Serotonin |
|---|
| Description | Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a molecule that belongs to the class of compounds known as indoleamines. An indoleamine consists of an indole ring that bears an amino group or an alkyl amino group attached to the indole ring. Serotonin has an aminoethyl at position 2 and a hydroxyl group at position 5 of the indole ring. Serotonin exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to plants to humans. In mammals, serotonin functions as a monoamine neurotransmitter, a biochemical messenger and regulator. It is synthesized from the essential amino acid L-Tryptophan. Approximately 90% of the human body's total serotonin is located in the enterochromaffin cells in the GI tract, where it regulates intestinal movements. About 8% is found in platelets and 1-2% in the CNS. Serotonin in the nervous system acts as a local transmitter at synapses, and as a paracrine or hormonal modulator of circuits upon diffusion, allowing a wide variety of "state-dependent" behavioral responses to different stimuli. Serotonin is widely distributed in the nervous system of vertebrates and invertebrates and some of its behavioral effects have been preserved along evolution. Such is the case of aggressive behavior and rhythmic motor patterns, including those responsible for feeding. In vertebrates, which display a wider and much more sophisticated behavioral repertoire, serotonin also modulates sleep, the arousal state, sexual behavior, and others. Deficiencies of the serotonergic system causes disorders such as depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, phobias, posttraumatic stress disorder, epilepsy, and generalized anxiety disorder. Serotonin has three different modes of action in the nervous system: as transmitter, acting locally at synaptic boutons; upon diffusion at a distance from its release sites, producing paracrine (also called volume) effects, and by circulating in the blood stream, producing hormonal effects. The three modes can affect a single neuronal circuit. (PMID: 16047543 ). Serotonin is also a microbial metabolite that can be found in the feces and urine of mammals. Urinary serotonin is produced by Candida, Streptococcus, Escherichia, and Enterococcus (PMID: 24621061 ). In plants, serotonin was first found and reported in a legume called Mucuna pruriens. The greatest concentration of serotonin in plants has been found in walnuts and hickory. In pineapples, banana, kiwi fruit, plums and tomatoes the concentration of serotonin is around 3 to 30 mg/kg. | Read more...
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C10H12N2O/c11-4-3-7-6-12-10-2-1-8(13)5-9(7)10/h1-2,5-6,12-13H,3-4,11H2 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 3-(2-Aminoethyl)-1H-indol-5-ol | ChEBI | | 5-HT | ChEBI | | 5-Hydroxytryptamine | ChEBI | | Enteramine | ChEBI | | Serotonine | ChEBI | | Thrombocytin | ChEBI | | Thrombotonin | ChEBI | | Hippophaine | HMDB | | Hydroxytryptamine | HMDB | | 5 Hydroxytryptamine | HMDB | | 3-(2-Aminoethyl)indol-5-ol | HMDB | | 3-(b-Aminoethyl)-5-hydroxyindole | HMDB | | 5-HTA | HMDB | | 5-Hydroxy-3-(b-aminoethyl)indole | HMDB | | 5-Hydroxy-tryptamine | HMDB | | 5-Hydroxyltryptamine | HMDB | | 5-Hydroxytriptamine | HMDB | | Antemovis | HMDB | | DS Substance | HMDB | | Enteramin | HMDB |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C10H12N2O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 176.2151 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 176.094963016 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 3-(2-aminoethyl)-1H-indol-5-ol |
|---|
| Traditional Name | serotonin |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 50-67-9 |
|---|
| SMILES | NCCC1=CNC2=C1C=C(O)C=C2 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C10H12N2O/c11-4-3-7-6-12-10-2-1-8(13)5-9(7)10/h1-2,5-6,12-13H,3-4,11H2 |
|---|
| InChI Key | QZAYGJVTTNCVMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as serotonins. Serotonins are compounds containing a serotonin moiety, which consists of an indole that bears an aminoethyl a position 2 and a hydroxyl group at position 5. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Indoles and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Tryptamines and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Serotonins |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Serotonin
- 3-alkylindole
- Hydroxyindole
- Indole
- 2-arylethylamine
- 1-hydroxy-2-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Aralkylamine
- Substituted pyrrole
- Benzenoid
- Pyrrole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Azacycle
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Amine
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 25.5 mg/mL | Human Metabolome Project | | LogP | 0.21 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| Serotonin,1TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2[NH]C=C(CCN)C2=C1 | 2027.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,1TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O)C=C12 | 2204.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,1TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N1C=C(CCN)C2=CC(O)=CC=C21 | 2111.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2123.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2282.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2418.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C | 2080.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C | 2154.9 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C | 2397.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C | 2350.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C | 2394.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C | 2606.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12 | 2221.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12 | 2301.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TMS,isomer #4 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12 | 2462.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2[NH]C=C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C2=C1 | 2358.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2[NH]C=C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C2=C1 | 2437.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2[NH]C=C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)C2=C1 | 2359.7 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2176.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2274.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TMS,isomer #2 | C[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2282.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C | 2405.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C | 2510.1 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TMS,isomer #3 | C[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C | 2385.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C | 2447.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C | 2437.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,4TMS,isomer #1 | C[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C | 2265.5 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2[NH]C=C(CCN)C2=C1 | 2312.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O)C=C12 | 2446.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N1C=C(CCN)C2=CC(O)=CC=C21 | 2369.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2678.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2699.0 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2603.2 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2570.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2547.8 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2542.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2802.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2798.2 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=C[NH]C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2694.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12 | 2693.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12 | 2724.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12 | 2597.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2[NH]C=C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=C1 | 3045.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2[NH]C=C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=C1 | 3035.3 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2[NH]C=C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=C1 | 2644.3 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2885.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2877.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)NCCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C=C12 | 2593.9 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3024.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3079.7 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)N(CCC1=CN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)C2=CC=C(O)C=C12)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2637.4 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3286.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3166.4 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | Serotonin,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(C)(C)[Si](C)(C)OC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(CCN([Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)=CN2[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2641.6 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (5 TMS) | splash10-00di-1900000000-461c2a1f67418e6b5d6a | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (5 TMS) | splash10-00di-1900000000-2286e87324e9f4a78cb4 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-1900000000-927b865023cbba872101 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-1910000000-02c17b4cd3336a8bf9b1 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (5 TMS) | splash10-00di-8900000000-4b838943ace80c8b7734 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (5 TMS) | splash10-00di-6900000000-a7dd5c569cf4d085d244 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (4 TMS) | splash10-00di-0900000000-2346e553f96cb980c8fc | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (3 TMS) | splash10-00di-1900000000-01fbd5196188d4e0f21c | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0002-9800000000-9ce9fb2286c3b7ea7719 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-1900000000-461c2a1f67418e6b5d6a | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-1900000000-2286e87324e9f4a78cb4 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-1900000000-927b865023cbba872101 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-1910000000-02c17b4cd3336a8bf9b1 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-8900000000-4b838943ace80c8b7734 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-6900000000-a7dd5c569cf4d085d244 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-0900000000-2346e553f96cb980c8fc | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-1900000000-01fbd5196188d4e0f21c | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-001j-6900000000-95a89ff8a3b12e7e8e25 | 2017-07-27 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-001i-9450000000-52e0b628b7795c643362 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Serotonin GC-MS (TBDMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin Linear Ion Trap , negative-QTOF | splash10-03di-1900000000-d64210214a1b3766ff6e | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-1900000000-66be80bf04de85d374b7 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-662e21ddee556bb4a222 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin 35V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-337ec7823cec887c8ad3 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-8ac1f8742228b0c2ada5 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00os-4900000000-fe28a76e9223ea9c3912 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00kf-9200000000-faf92490b8049363f990 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0006-9500000000-c65e4440ede6c6f45d71 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-6acaf73bcd452e24b886 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0aor-0900000000-259227b20b82e6362059 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-02e9-5900000000-2f58fbed270523182158 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin EI-B (HITACHI M-80) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-0002-9800000000-abcd0769bb17d07b3e38 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-bf65d809200ea387ebf5 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-8a171ac4fdc0474f7f48 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03xr-0900000000-a0b7d8a671909c6f4ad1 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014i-1900000000-fa80d05236eabbafd678 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014i-4900000000-4e2e322d56fc9ee00edd | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Positive-QTOF | splash10-004i-0900000000-c79f0b03a8dc1da0a10a | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) 30V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-03fr-0900000000-9cb056cd56bae76589d0 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QTOF , positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-08840bc938c367dacbb2 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QTOF , positive-QTOF | splash10-03yi-0900000000-858936972fd87c0c0b14 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QTOF , positive-QTOF | splash10-0159-4900000000-a8fc7dff385a4f51b88a | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QTOF , positive-QTOF | splash10-00p0-9400000000-7e4063d2b516ae59df84 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-bf65d809200ea387ebf5 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Serotonin LC-ESI-QQ , positive-QTOF | splash10-03di-0900000000-8a171ac4fdc0474f7f48 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-16 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Feces
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Adipose Tissue
- Adrenal Cortex
- Adrenal Gland
- Adrenal Medulla
- Bladder
- Brain
- Epidermis
- Fibroblasts
- Intestine
- Kidney
- Neuron
- Pancreas
- Placenta
- Platelet
- Prostate
- Skeletal Muscle
|
|---|
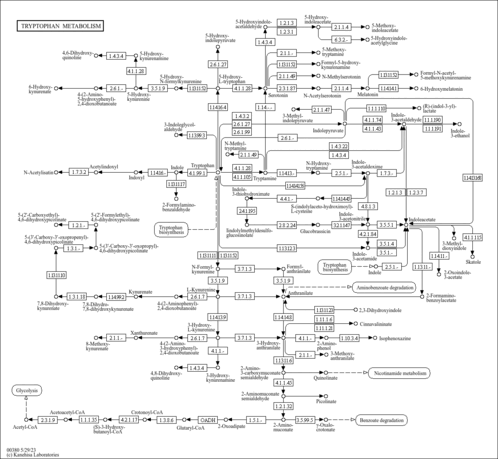
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.85 +/- 0.077 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.07 (0-0.15) uM | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.70 +/- 0.32 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.74 +/- 0.28 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.97 +/- 0.28 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.30-2.00 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.41 +/- 0.33 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.14(0.72-1.72) uM | Children (1-13 uears old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0057-0.012 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0053-0.01 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.001 (0.0006-0.002) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.002-0.025 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.00001 +/- 0.000002 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0059 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.026 (0.017-0.040) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | - Geigy Scientific ...
- West Cadwell, N.J...
- Basel, Switzerlan...
| details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.02 (0.004-0.0315) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | - Geigy Scientific ...
- West Cadwell, N.J...
- Basel, Switzerlan...
| details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.1512 +/- 0.0566 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.1-0.35 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.20 +/- 0.07 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.2 +/- 0.05 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.065 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 9.892 +/- 3.264 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.12 (0.10-0.15) umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.0110-0.0680 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.03 (0.015-0.046) umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | - Geigy Scientific ...
- West Cadwell, N.J...
- Basel, Switzerlan...
| details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.08 (0.04-0.12) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.0350-0.0670 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Female | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.61 +/- 0.096 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Schizophrenia | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.4(0.96-1.98) uM | Children (1-13 uears old) | Both | Environmental enteric dysfunction | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | <0.002 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Male | sepiapterin reductase deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.00001 +/- 0.0000036 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Hypothyroidism | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.0044 (0.00-0.0093) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Parkinson's Disease | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.00001 +/- 0.000004 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Hypothyroidism | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal Cancer | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.1758 +/- 0.057 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Eosinophilic esophagitis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.1782 +/- 0.0798 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Gastroesophageal reflux disease | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 3.755 +/- 3.583 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Eosinophilic esophagitis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.124-0.233 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Brunner Syndrome | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.188 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Female | Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.221 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Female | Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Schizophrenia |
|---|
- Fukushima T, Iizuka H, Yokota A, Suzuki T, Ohno C, Kono Y, Nishikiori M, Seki A, Ichiba H, Watanabe Y, Hongo S, Utsunomiya M, Nakatani M, Sadamoto K, Yoshio T: Quantitative analyses of schizophrenia-associated metabolites in serum: serum D-lactate levels are negatively correlated with gamma-glutamylcysteine in medicated schizophrenia patients. PLoS One. 2014 Jul 8;9(7):e101652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101652. eCollection 2014. [PubMed:25004141 ]
| | Parkinson's disease |
|---|
- Engelborghs S, Marescau B, De Deyn PP: Amino acids and biogenic amines in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Res. 2003 Aug;28(8):1145-50. [PubMed:12834252 ]
| | Hypothyroidism |
|---|
- Sjoberg S, Eriksson M, Nordin C: L-thyroxine treatment and neurotransmitter levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of hypothyroid patients: a pilot study. Eur J Endocrinol. 1998 Nov;139(5):493-7. [PubMed:9849813 ]
| | Sepiapterin reductase deficiency |
|---|
- Verbeek MM, Willemsen MA, Wevers RA, Lagerwerf AJ, Abeling NG, Blau N, Thony B, Vargiami E, Zafeiriou DI: Two Greek siblings with sepiapterin reductase deficiency. Mol Genet Metab. 2008 Aug;94(4):403-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2008.04.003. Epub 2008 May 27. [PubMed:18502672 ]
| | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Brown DG, Rao S, Weir TL, O'Malia J, Bazan M, Brown RJ, Ryan EP: Metabolomics and metabolic pathway networks from human colorectal cancers, adjacent mucosa, and stool. Cancer Metab. 2016 Jun 6;4:11. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0151-y. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27275383 ]
| | Eosinophilic esophagitis |
|---|
- Slae, M., Huynh, H., Wishart, D.S. (2014). Analysis of 30 normal pediatric urine samples via NMR spectroscopy (unpublished work). NA.
| | Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency |
|---|
- Abeling NG, van Gennip AH, Barth PG, van Cruchten A, Westra M, Wijburg FA: Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: a new case with a mild clinical presentation and unexpected laboratory findings. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1998 Jun;21(3):240-2. [PubMed:9686366 ]
| | Brunner Syndrome |
|---|
- Brunner HG, Nelen MR, van Zandvoort P, Abeling NG, van Gennip AH, Wolters EC, Kuiper MA, Ropers HH, van Oost BA: X-linked borderline mental retardation with prominent behavioral disturbance: phenotype, genetic localization, and evidence for disturbed monoamine metabolism. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1032-9. [PubMed:8503438 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 181500 (Schizophrenia)
- 168600 (Parkinson's disease)
- 182125 (Sepiapterin reductase deficiency)
- 114500 (Colorectal cancer)
- 610247 (Eosinophilic esophagitis)
- 608643 (Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency)
- 300615 (Brunner Syndrome)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB08839 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB012158 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00001429 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 5013 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00780 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | SEROTONIN |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Serotonin |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 5202 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 28790 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | SRTN |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000126 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Harley-Mason, John; Jackson, A. H. Hydroxytryptamines. I. Bufotenine, 6-hydroxybufotenine, and serotonin. Journal of the Chemical Society (1954), 1165-71. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Cozzi A, Zignego AL, Carpendo R, Biagiotti T, Aldinucci A, Monti M, Giannini C, Rosselli M, Laffi G, Moroni F: Low serum tryptophan levels, reduced macrophage IDO activity and high frequency of psychopathology in HCV patients. J Viral Hepat. 2006 Jun;13(6):402-8. [PubMed:16842443 ]
- Engelborghs S, Marescau B, De Deyn PP: Amino acids and biogenic amines in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Res. 2003 Aug;28(8):1145-50. [PubMed:12834252 ]
- Panholzer TJ, Beyer J, Lichtwald K: Coupled-column liquid chromatographic analysis of catecholamines, serotonin, and metabolites in human urine. Clin Chem. 1999 Feb;45(2):262-8. [PubMed:9931050 ]
- King BM: The rise, fall, and resurrection of the ventromedial hypothalamus in the regulation of feeding behavior and body weight. Physiol Behav. 2006 Feb 28;87(2):221-44. Epub 2006 Jan 18. [PubMed:16412483 ]
- Sjoberg S, Eriksson M, Nordin C: L-thyroxine treatment and neurotransmitter levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of hypothyroid patients: a pilot study. Eur J Endocrinol. 1998 Nov;139(5):493-7. [PubMed:9849813 ]
- Eklundh T, Eriksson M, Sjoberg S, Nordin C: Monoamine precursors, transmitters and metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid: a prospective study in healthy male subjects. J Psychiatr Res. 1996 May-Jun;30(3):201-8. [PubMed:8884658 ]
- Serebruany VL, Glassman AH, Malinin AI, Nemeroff CB, Musselman DL, van Zyl LT, Finkel MS, Krishnan KR, Gaffney M, Harrison W, Califf RM, O'Connor CM: Platelet/endothelial biomarkers in depressed patients treated with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline after acute coronary events: the Sertraline AntiDepressant Heart Attack Randomized Trial (SADHART) Platelet Substudy. Circulation. 2003 Aug 26;108(8):939-44. Epub 2003 Aug 11. [PubMed:12912814 ]
- Preuss HG, Garis RI, Bramble JD, Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Rao CV, Satyanarayana S: Efficacy of a novel calcium/potassium salt of (-)-hydroxycitric acid in weight control. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res. 2005;25(3):133-44. [PubMed:16366421 ]
- Lincoln J, Crowe R, Kamm MA, Burnstock G, Lennard-Jones JE: Serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid are increased in the sigmoid colon in severe idiopathic constipation. Gastroenterology. 1990 May;98(5 Pt 1):1219-25. [PubMed:1691117 ]
- Lundeberg L, Liang Y, Sundstrom E, Nordlind K, Verhofstad A, Liden S, Johansson O: Serotonin in human allergic contact dermatitis. An immunohistochemical and high-performance liquid chromatographic study. Arch Dermatol Res. 1999 May;291(5):269-74. [PubMed:10367709 ]
- Blardi P, Palazzuoli A, de Lalla A, Auteri A: Variations of peripheral markers of serotoninergic system in selected vascular patients. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2006 Apr;16(3):210-4. Epub 2005 Oct 21. [PubMed:16580588 ]
- Lommatzsch M, Hornych K, Zingler C, Schuff-Werner P, Hoppner J, Virchow JC: Maternal serum concentrations of BDNF and depression in the perinatal period. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2006 Apr;31(3):388-94. Epub 2005 Nov 10. [PubMed:16289360 ]
- Koskiniemi M, Laakso J, Kuurne T, Laipio M, Harkonen M: Indole levels in human lumbar and ventricular cerebrospinal fluid and the effect of L-tryptophan administration. Acta Neurol Scand. 1985 Feb;71(2):127-32. [PubMed:2580417 ]
- Lawrence KR, Adra M, Gillman PK: Serotonin toxicity associated with the use of linezolid: a review of postmarketing data. Clin Infect Dis. 2006 Jun 1;42(11):1578-83. Epub 2006 Apr 27. [PubMed:16652315 ]
- Blardi P, de Lalla A, Pieragalli D, De Franco V, Meini S, Ceccatelli L, Auteri A: Effect of iloprost on plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine and plasma and platelet serotonin in patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2006 Sep;80(3-4):175-82. Epub 2006 Jul 18. [PubMed:16939882 ]
- Eriksson O, Wall A, Marteinsdottir I, Agren H, Hartvig P, Blomqvist G, Langstrom B, Naessen T: Mood changes correlate to changes in brain serotonin precursor trapping in women with premenstrual dysphoria. Psychiatry Res. 2006 Mar 31;146(2):107-16. Epub 2006 Mar 2. [PubMed:16515859 ]
- Ormazabal A, Vilaseca MA, Perez-Duenas B, Lambruschini N, Gomez L, Campistol J, Artuch R: Platelet serotonin concentrations in PKU patients under dietary control and tetrahydrobiopterin treatment. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2005;28(6):863-70. [PubMed:16435178 ]
- Ortiz J, Artigas F, Gelpi E: Serotonergic status in human blood. Life Sci. 1988;43(12):983-90. [PubMed:2459577 ]
- Sato T, Suzuki E, Yokoyama M, Semba J, Watanabe S, Miyaoka H: Chronic intraperitoneal injection of interferon-alpha reduces serotonin levels in various regions of rat brain, but does not change levels of serotonin transporter mRNA, nitrite or nitrate. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2006 Aug;60(4):499-506. [PubMed:16884454 ]
- Konca K, Tiftik EN, Aslan G, Kanik A, Yalcin A: The effect of cromoglycate on time-dependent histamine and serotonin concentrations in stored blood products. Transfus Apher Sci. 2006 Apr;34(2):193-8. Epub 2006 Mar 3. [PubMed:16516555 ]
- De-Miguel FF, Trueta C: Synaptic and extrasynaptic secretion of serotonin. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2005 Mar;25(2):297-312. [PubMed:16047543 ]
- Mezzelani A, Landini M, Facchiano F, Raggi ME, Villa L, Molteni M, De Santis B, Brera C, Caroli AM, Milanesi L, Marabotti A: Environment, dysbiosis, immunity and sex-specific susceptibility: a translational hypothesis for regressive autism pathogenesis. Nutr Neurosci. 2015 May;18(4):145-61. doi: 10.1179/1476830513Y.0000000108. Epub 2014 Jan 21. [PubMed:24621061 ]
| Show more...
|---|