| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2022-03-07 02:48:59 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000215 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | - HMDB0000533
- HMDB0014288
- HMDB00215
- HMDB00533
- HMDB14288
| Show more accession numbers
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine |
|---|
| Description | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine, also known as glcnac or N-acetylchitosamine, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acylaminosugars. These are organic compounds containing a sugar linked to a chain through N-acyl group. O-N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine regulates cellular responses to hormones such as insulin, initiates a protective response to stress, modulates a cell's capacity to grow and divide, and regulates gene transcription. N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine is an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans. In humans, it exists in skin, cartilage and blood vessel as a component of hyaluronic acid, and bone tissue, cornea and aorta as a component of keratan sulfate. Within humans, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine can be biosynthesized from chitobiose through the action of the enzyme Beta-hexosaminidase subunit alpha. In addition, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine can be biosynthesized from chitin through the action of the enzyme chitotriosidase-1. O-N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine modified proteins are involved in sensing the nutrient status of the surrounding cellular environment and adjusting the activity of cellular proteins accordingly. In humans, N-acetyl-D-glucosamine is involved in the metabolic disorder called the salla disease/infantile sialic acid storage disease pathway. Outside of the human body, N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine is found, on average, in the highest concentration within milk (cow). N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine has also been detected, but not quantified in, peachs. This could make N-acetyl-D-glucosamine a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. Chemically it is an amide between glucosamine and acetic acid. N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine (N-acetlyglucosamine) is a monosaccharide derivative of glucose. A single N-acetlyglucosamine moiety linked to serine or threonine residues on nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins -O-GlcNAc, is an ubiquitous post-translational protein modification. | Read more...
|---|
| Structure | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O InChI=1S/C8H15NO6/c1-3(11)9-5-7(13)6(12)4(2-10)15-8(5)14/h4-8,10,12-14H,2H2,1H3,(H,9,11)/t4-,5-,6-,7-,8?/m1/s1 |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose | ChEBI | | GlcNAc | ChEBI | | N-Acetylchitosamine | ChEBI | | 2-(Acetylamino)-2-deoxyhexose | HMDB | | 2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucopyranose | HMDB | | 2-Acetamido-2-deoxyglucose | HMDB | | 2-Acetamido-D-glucose | HMDB | | 2-Acetylamino-2-deoxy-D-glucose | HMDB | | Acetylglucosamine | HMDB | | N-Acetylglucosamine | HMDB | | N-[(3R,4R,5S,6R)-2,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]acetamide | HMDB | | 2 Acetamido 2 deoxyglucose | HMDB | | N Acetyl D glucosamine | HMDB | | 2 Acetamido 2 deoxy D glucose | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C8H15NO6 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 221.2078 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 221.089937217 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | N-[(3R,4R,5S,6R)-2,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]acetamide |
|---|
| Traditional Name | GlcNAc |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 7512-17-6 |
|---|
| SMILES | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C8H15NO6/c1-3(11)9-5-7(13)6(12)4(2-10)15-8(5)14/h4-8,10,12-14H,2H2,1H3,(H,9,11)/t4-,5-,6-,7-,8?/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | OVRNDRQMDRJTHS-RTRLPJTCSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acylaminosugars. These are organic compounds containing a sugar linked to a chain through N-acyl group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Acylaminosugars |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Acylaminosugar
- N-acyl-alpha-hexosamine
- Hexose monosaccharide
- Monosaccharide
- Oxane
- Acetamide
- Carboxamide group
- Hemiacetal
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Polyol
- Alcohol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | Not Available |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 210 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 167 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | -2.1 | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Experimental Collision Cross Sections |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized| Derivative Name / Structure | SMILES | Kovats RI Value | Column Type | Reference |
|---|
| N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,1TMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 1917.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,1TMS,isomer #2 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 1928.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,1TMS,isomer #3 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 1918.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,1TMS,isomer #4 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 1920.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,1TMS,isomer #5 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1860.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 1940.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TMS,isomer #10 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1912.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TMS,isomer #2 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 1941.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TMS,isomer #3 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 1939.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TMS,isomer #4 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1932.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TMS,isomer #5 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 1963.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TMS,isomer #6 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 1968.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TMS,isomer #7 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1935.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TMS,isomer #8 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 1959.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TMS,isomer #9 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1914.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2002.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TMS,isomer #10 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1974.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TMS,isomer #2 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2016.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TMS,isomer #3 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1972.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TMS,isomer #4 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2010.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TMS,isomer #5 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1983.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TMS,isomer #6 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1997.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TMS,isomer #7 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2026.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TMS,isomer #8 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 1980.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TMS,isomer #9 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 1975.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,4TMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C | 2037.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,4TMS,isomer #2 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C | 2042.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,4TMS,isomer #3 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2048.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,4TMS,isomer #4 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2047.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,4TMS,isomer #5 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2040.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,5TMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2091.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,5TMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2155.6 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,5TMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C | 2099.0 | Standard polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,1TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2175.9 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,1TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2176.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,1TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2179.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,1TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2182.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,1TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2137.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O | 2419.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2386.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2438.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2432.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2396.2 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2435.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2452.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2414.8 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2433.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,2TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2398.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O | 2686.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TBDMS,isomer #10 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2631.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2672.0 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2631.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2662.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2643.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TBDMS,isomer #6 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2634.5 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TBDMS,isomer #7 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2695.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TBDMS,isomer #8 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2657.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,3TBDMS,isomer #9 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2648.6 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,4TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N[C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2889.4 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,4TBDMS,isomer #2 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2867.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,4TBDMS,isomer #3 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2860.1 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,4TBDMS,isomer #4 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2853.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,4TBDMS,isomer #5 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2865.7 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3094.3 | Semi standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 3054.5 | Standard non polar | 33892256 | | N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine,5TBDMS,isomer #1 | CC(=O)N([C@H]1C(O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)O[C@H](CO[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H](O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[C@@H]1O[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C)[Si](C)(C)C(C)(C)C | 2695.8 | Standard polar | 33892256 |
| Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0ktb-1931000000-1c4cb4ec9b01c3571b7d | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0ktb-0931000000-943fefe13d3449a92db7 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0f9j-1930000000-388fd70c48f209a58653 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-9620000000-1fd16b8e8608db3ef657 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-9620000000-ceed8b621b338130ce76 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-9620000000-8a3ade37d256b2bd4585 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0ktb-1931000000-1c4cb4ec9b01c3571b7d | 2018-05-18 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0ktb-0931000000-943fefe13d3449a92db7 | 2018-05-18 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0f9j-1930000000-388fd70c48f209a58653 | 2018-05-18 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-9620000000-1fd16b8e8608db3ef657 | 2018-05-18 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-9620000000-ceed8b621b338130ce76 | 2018-05-18 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00di-9620000000-8a3ade37d256b2bd4585 | 2018-05-18 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0ue9-6920000000-c07df80c6fb758af9cd2 | 2017-09-01 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (4 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0007-3332900000-ee533266929b5b95ee4d | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (TMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (TMS_1_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (TMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (TMS_2_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (TMS_2_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (TMS_2_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine GC-MS (TMS_2_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0pb9-9800000000-d2628c9d8baf55923bf5 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 35V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0pb9-9500000000-76ab0b7c683cc252741d | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 35V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0pb9-9400000000-5b6f61c6f220e75c6736 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 35V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0pb9-9500000000-17fd92d5a45dc38915af | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9300000000-ccb575a1c77c8addd5fe | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 35V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0pb9-9500000000-bf8c7a4f84891bcf3eb2 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 35V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-f38ecd220da0924d093c | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0ab9-9400000000-eaa89be4aad99c7a4503 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 35V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-3900000000-819a6ad0f73785d9287c | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-000i-1910000000-723db02c59f390b489a7 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0537-9000000000-735f54db3223e736c337 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-003e-9600000000-197c8bc76e52b96b9871 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00di-1490000000-40dfe33adabe6ad7a7a8 | 2015-09-14 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0il0-2940000000-880c7b1fb58ed63f0ee2 | 2015-09-14 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-01ox-9400000000-e1f07558d7921e9f24e1 | 2015-09-14 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-05g0-8920000000-d504941e0508d1593f33 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0pb9-9820000000-753556be259b7e745ba7 | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9100000000-bad102d081eb3bbc006b | 2015-09-15 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9500000000-2c2b09cb6bfb29039085 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0abc-9540000000-a1f7d557237a521d306a | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-18eabe9e3d3657888360 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0udi-0390000000-3820a7eec5a8c72f49d9 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0h90-9740000000-db880363194a3979c637 | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0229-9200000000-cdcf015aa799dc7d6d8b | 2021-09-24 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | 2021-09-29 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Membrane
- Lysosome
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Breast Milk
- Feces
- Saliva
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | - Intestine
- Neuron
- Placenta
- Platelet
- Prostate
|
|---|
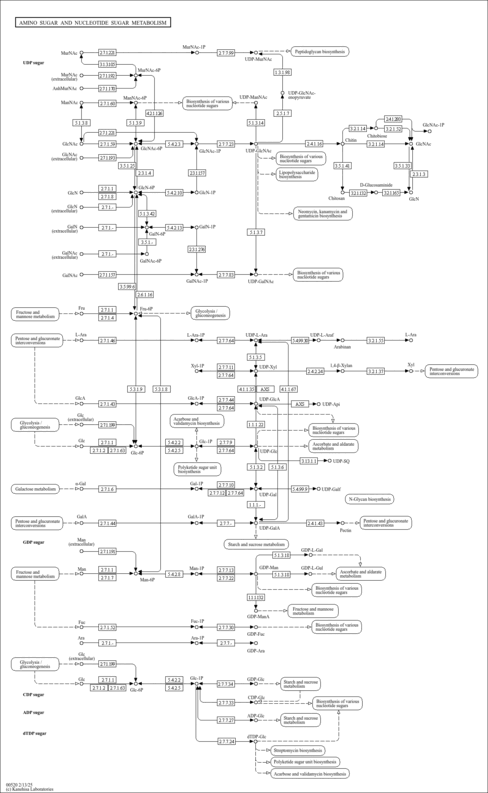
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Expected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Available | Not Available | Normal | | details | | Breast Milk | Detected and Quantified | 204.3278984 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Not Specified | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 2.23 +/- 1.83 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 2.40 +/- 2.35 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 21.4 +/- 18.6 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 3.14 +/- 2.38 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 3.78 +/- 3.93 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Saliva | Detected and Quantified | 4.41 +/- 5.98 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.96 +/- 1.85 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal Cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | asymptomatic diverticulosis | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Colorectal cancer | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Bladder cancer | | details |
|
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Colorectal cancer |
|---|
- Brown DG, Rao S, Weir TL, O'Malia J, Bazan M, Brown RJ, Ryan EP: Metabolomics and metabolic pathway networks from human colorectal cancers, adjacent mucosa, and stool. Cancer Metab. 2016 Jun 6;4:11. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0151-y. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27275383 ]
- Sinha R, Ahn J, Sampson JN, Shi J, Yu G, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Goedert JJ: Fecal Microbiota, Fecal Metabolome, and Colorectal Cancer Interrelations. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 25;11(3):e0152126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152126. eCollection 2016. [PubMed:27015276 ]
- Goedert JJ, Sampson JN, Moore SC, Xiao Q, Xiong X, Hayes RB, Ahn J, Shi J, Sinha R: Fecal metabolomics: assay performance and association with colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2089-96. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu131. Epub 2014 Jul 18. [PubMed:25037050 ]
| | Diverticular disease |
|---|
- Tursi A, Mastromarino P, Capobianco D, Elisei W, Miccheli A, Capuani G, Tomassini A, Campagna G, Picchio M, Giorgetti G, Fabiocchi F, Brandimarte G: Assessment of Fecal Microbiota and Fecal Metabolome in Symptomatic Uncomplicated Diverticular Disease of the Colon. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016 Oct;50 Suppl 1:S9-S12. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000626. [PubMed:27622378 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB008032 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 388319 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00140 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 34006 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 3356 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 439174 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 506227 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | ACGAM |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Zhang, He; Qi, Shanlong; Yang, Shenggui. Production of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine from chitin. Faming Zhuanli Shenqing Gongkai Shuomingshu (2006), 6pp. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM, Khan AP, Cao Q, Yu J, Laxman B, Mehra R, Lonigro RJ, Li Y, Nyati MK, Ahsan A, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Han B, Cao X, Byun J, Omenn GS, Ghosh D, Pennathur S, Alexander DC, Berger A, Shuster JR, Wei JT, Varambally S, Beecher C, Chinnaiyan AM: Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature. 2009 Feb 12;457(7231):910-4. doi: 10.1038/nature07762. [PubMed:19212411 ]
- Nakagawa F, Schulte BA, Spicer SS: Lectin cytochemical evaluation of somatosensory neurons and their peripheral and central processes in rat and man. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;245(3):579-89. [PubMed:3757018 ]
- Hatcher VB, Schwarzmann GO, Jeanloz RW, McArthur JW: Changes in the sialic acid concentration in the major cervical glycoprotein from the bonnet monkey (Macaca radiata) during a hormonally induced cycle. Fertil Steril. 1977 Jun;28(6):682-8. [PubMed:405259 ]
- Percheron F: [Beta-D-mannosidase]. Bull Acad Natl Med. 1995 May;179(5):881-91; discussion 892. [PubMed:7583460 ]
- Collard CD, Montalto MC, Reenstra WR, Buras JA, Stahl GL: Endothelial oxidative stress activates the lectin complement pathway: role of cytokeratin 1. Am J Pathol. 2001 Sep;159(3):1045-54. [PubMed:11549596 ]
- Mollicone R, Candelier JJ, Mennesson B, Couillin P, Venot AP, Oriol R: Five specificity patterns of (1----3)-alpha-L-fucosyltransferase activity defined by use of synthetic oligosaccharide acceptors. Differential expression of the enzymes during human embryonic development and in adult tissues. Carbohydr Res. 1992 Apr 10;228(1):265-76. [PubMed:1366057 ]
- Kottgen E, Hell B, Muller C, Kainer F, Tauber R: Developmental changes in the glycosylation and binding properties of human fibronectins. Characterization of the glycan structures and ligand binding of human fibronectins from adult plasma, cord blood and amniotic fluid. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1989 Dec;370(12):1285-94. [PubMed:2619923 ]
- Madrid JF, Castells MT, Martinez-Menarguez JA, Aviles M, Hernandez F, Ballesta J: Subcellular characterization of glycoproteins in the principal cells of human gallbladder. A lectin cytochemical study. Histochemistry. 1994 Mar;101(3):195-204. [PubMed:8056619 ]
- Weiner B, Fischer T, Waxman S: Hemostasis in the era of the chronic anticoagulated patient. J Invasive Cardiol. 2003 Nov;15(11):669-73; quiz 674. [PubMed:14608143 ]
- Yates AD, Watkins WM: Enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of glycoconjugates. A UDP-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-D-glucose: beta-D-galactopyranosyl-(1 leads to 4)-saccharide (1 leads to 3)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D- glucopyranosyltransferase in human serum. Carbohydr Res. 1983 Aug 16;120:251-68. [PubMed:6226355 ]
- Slawson C, Housley MP, Hart GW: O-GlcNAc cycling: how a single sugar post-translational modification is changing the way we think about signaling networks. J Cell Biochem. 2006 Jan 1;97(1):71-83. [PubMed:16237703 ]
- Elshenawy S, Pinney SE, Stuart T, Doulias PT, Zura G, Parry S, Elovitz MA, Bennett MJ, Bansal A, Strauss JF 3rd, Ischiropoulos H, Simmons RA: The Metabolomic Signature of the Placenta in Spontaneous Preterm Birth. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3). pii: ijms21031043. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031043. [PubMed:32033212 ]
| Show more...
|---|