| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 5.0 |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Quantified |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2005-11-16 15:48:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2023-05-30 20:55:53 UTC |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000202 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | |
|---|
| Metabolite Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Methylmalonic acid |
|---|
| Description | Methylmalonic acid is a malonic acid derivative, which is a vital intermediate in the metabolism of fat and protein. In particular, the coenzyme A-linked form of methylmalonic acid, methylmalonyl-CoA, is converted into succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase in a reaction that requires vitamin B12 as a cofactor. In this way, methylmalonic acid enters the Krebs cycle and is thus part of one of the anaplerotic reactions. Abnormalities in methylmalonic acid metabolism lead to methylmalonic aciduria. This inborn error of metabolism is attributed to a block in the enzymatic conversion of methylmalonyl CoA to succinyl CoA. Methylmalonic acid is also found to be associated with other inborn errors of metabolism, including cobalamin deficiency, cobalamin malabsorption, malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency, and transcobalamin II deficiency. When present in sufficiently high levels, methylmalonic acid can act as an acidogen and a metabotoxin. An acidogen is an acidic compound that induces acidosis, which has multiple adverse effects on many organ systems. A metabotoxin is an endogenously produced metabolite that causes adverse health effects at chronically high levels. Chronically high levels of methylmalonic acid are associated with at least 5 inborn errors of metabolism, including Malonyl CoA decarboxylase deficiency, Malonic Aciduria, Methylmalonate Semialdehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency, Methylmalonic Aciduria and Methylmalonic Aciduria Due to Cobalamin-Related Disorders. Methylmalonic acid is an organic acid and abnormally high levels of organic acids in the blood (organic acidemia), urine (organic aciduria), the brain, and other tissues lead to general metabolic acidosis. Acidosis typically occurs when arterial pH falls below 7.35. In infants with acidosis, the initial symptoms include poor feeding, vomiting, loss of appetite, weak muscle tone (hypotonia), and lack of energy (lethargy). These can progress to heart abnormalities, kidney abnormalities, liver damage, seizures, coma, and possibly death. These are also the characteristic symptoms of the untreated IEMs mentioned above. Many affected children with organic acidemias experience intellectual disability or delayed development. In adults, acidosis or acidemia is characterized by headaches, confusion, feeling tired, tremors, sleepiness, and seizures. | Read more...
|---|
| Structure | InChI=1S/C4H6O4/c1-2(3(5)6)4(7)8/h2H,1H3,(H,5,6)(H,7,8) |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 1,1-Ethanedicarboxylic acid | ChEBI | | 2-Methylmalonic acid | ChEBI | | alpha-Methylmalonic acid | ChEBI | | Isosuccinic acid | ChEBI | | 1,1-Ethanedicarboxylate | Generator | | 2-Methylmalonate | Generator | | a-Methylmalonate | Generator | | a-Methylmalonic acid | Generator | | alpha-Methylmalonate | Generator | | Α-methylmalonate | Generator | | Α-methylmalonic acid | Generator | | Isosuccinate | Generator | | Methylmalonate | Generator | | Methyl-malonate | HMDB | | Methyl-malonic acid | HMDB | | Methyl-propanedioate | HMDB | | Methyl-propanedioic acid | HMDB | | Methylpropanedioate | HMDB | | Methylpropanedioic acid | HMDB | | Acid, methylmalonic | HMDB | | Methylmalonic acid | KEGG |
| Show more...
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C4H6O4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 118.088 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 118.02660868 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-methylpropanedioic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | methylmalonic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 516-05-2 |
|---|
| SMILES | CC(C(O)=O)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C4H6O4/c1-2(3(5)6)4(7)8/h2H,1H3,(H,5,6)(H,7,8) |
|---|
| InChI Key | ZIYVHBGGAOATLY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as dicarboxylic acids and derivatives. These are organic compounds containing exactly two carboxylic acid groups. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Dicarboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Dicarboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 1,3-dicarbonyl compound
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
| Physiological effect | |
|---|
| Disposition | |
|---|
| Process | |
|---|
| Role | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Molecular Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 135 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 679 mg/mL | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Experimental Chromatographic Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Predicted Molecular Properties | | Show more...
|---|
| Predicted Chromatographic Properties | Predicted Collision Cross SectionsPredicted Kovats Retention IndicesUnderivatizedDerivatized | Show more...
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| GC-MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (2 TMS) | splash10-0002-1910000000-cf95dd8a481761a28664 | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (2 TMS) | splash10-006t-8900000000-4d8795e7e4300cc7ceff | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-MS (2 TMS) | splash10-00lr-5940000000-56b86ada220d335ce30a | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-MS (3 TMS) | splash10-001i-9301000000-54e5247d046de566ac1e | 2014-06-16 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-004i-9000000000-b9ee59dddf90dfc7c461 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0002-1910000000-cf95dd8a481761a28664 | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-006t-8900000000-4d8795e7e4300cc7ceff | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-001i-9301000000-54e5247d046de566ac1e | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00lr-5940000000-56b86ada220d335ce30a | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Experimental GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0002-0900000000-684a11ce99cccbd9194a | 2017-09-12 | HMDB team, MONA, MassBank | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0g4i-9400000000-baa4ea6d613ebb8bffc7 | 2016-09-22 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-MS (2 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00dr-9310000000-a99f1bb4adbde62446d9 | 2017-10-06 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid GC-MS (TBDMS_2_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-05di-9000000000-8d09b408489f7b1743b5 | 2014-09-20 | Not Available | View Spectrum |
MS/MS Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid Quattro_QQQ 10V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-00di-9000000000-1578bea9a6b8b12e2f9b | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid Quattro_QQQ 25V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-05fr-9000000000-0e443f81ee9c6c9b1fa5 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid Quattro_QQQ 40V, Negative-QTOF (Annotated) | splash10-0ab9-9100000000-d23d6a0a35141ed9a950 | 2012-07-24 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-01b9-6900000000-6d969044a89f00e1b46f | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000000000-0f655174050263224e67 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0ab9-9000000000-26a654fb133b28a816a0 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-7afd566e443d5fa38887 | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-5c4795e954d5c3e9b74e | 2012-08-31 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-01b9-6900000000-6d969044a89f00e1b46f | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000000000-0f655174050263224e67 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-0ab9-9000000000-26a654fb133b28a816a0 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-7afd566e443d5fa38887 | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid LC-ESI-QQ , negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-5c4795e954d5c3e9b74e | 2017-09-14 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-175b62a78de8d2295d7c | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-00dm-9100000000-2118d1ea1507076c595c | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0007-9000000000-5ead13e9a754843f3de4 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9000000000-04818c3d6cdaf0e910eb | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-052f-9000000000-ea4a508808f00639e8c2 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Experimental LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-0002-9100000000-e8e132c8d454aa8a0490 | 2021-09-20 | HMDB team, MONA | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 10V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-014i-5900000000-9b75ec910fa494f0ad6a | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 20V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-05di-9200000000-87a71ae13cf70d990bb1 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 40V, Positive-QTOF | splash10-004i-9000000000-e7ae04912b5ee745a992 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 10V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-014i-4900000000-0714f0bc5c29e5d61ac4 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 20V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-00di-9100000000-ecfebddbd3d8f7224994 | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Methylmalonic acid 40V, Negative-QTOF | splash10-05fr-9000000000-506ee5ec2100e13e09ce | 2016-09-12 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
NMR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Experimental 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-04 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2021-10-10 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum | | Experimental 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | 2012-12-05 | Wishart Lab | View Spectrum |
IR Spectra| Spectrum Type | Description | Deposition Date | Source | View |
|---|
| Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M-H]-) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+H]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum | | Predicted IR Spectrum | IR Ion Spectrum (Predicted IRIS Spectrum, Adduct: [M+Na]+) | 2023-02-03 | FELIX lab | View Spectrum |
| Show more...
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm (predicted from logP)
|
|---|
| Biospecimen Locations | - Blood
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Feces
- Urine
|
|---|
| Tissue Locations | |
|---|
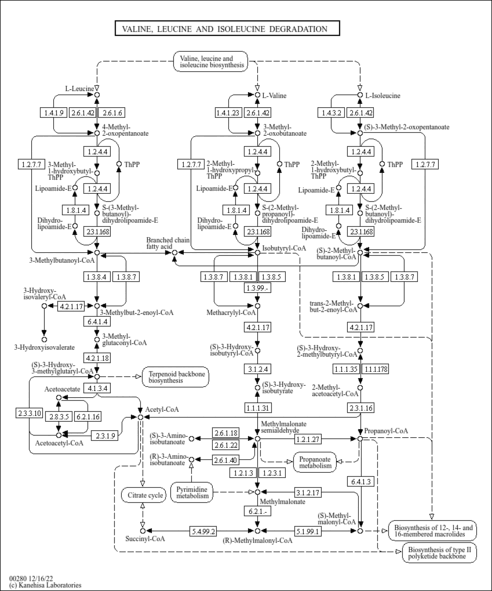
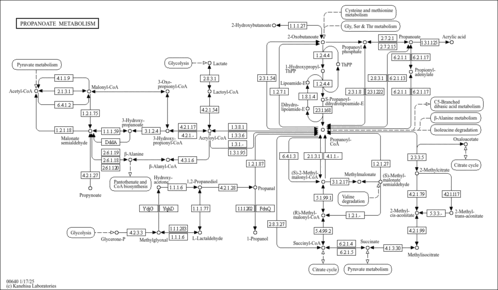
| Pathways | |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.14 (0.04-0.26) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.187 +/- 0.084 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | <0.28 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | <0.33 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | <0.4 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | <0.27 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.17 (0.073-0.27) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | <0.34 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.200 (0.00-0.400) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.15-0.55 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.40 (0.16-0.59) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.51 +/- 0.13 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.32 +/- 0.11 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Feces | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <3 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <5.130 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.42-19.74 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.28(0.52-6.64) umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.89(0.42-22.51) umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 3.495 +/- 2.595 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Not Available | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 9.247 +/- 8.216 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.92 +/- 1.97 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0-1.8 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0-1.9 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0-3.1 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0-4.3 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.58 (0.0-3.29) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.0 +/- 0.7 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 4.0 +/- 0.9 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.7-2.8 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Female | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <5.13 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.8 (0.00-3.6) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.50 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.9 (0.7-3.5) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.87 (0.36-1.23) umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.64 +/- 0.39 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.17 +/- 0.11 umol/mmol creatinine | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 2.51 +/- 1.01 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <0.07 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <47.871 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <6 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 3.086 +/- 1.081 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.5-2.4 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Male | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.765 +/- 0.896 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.6 (0-3.6) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 9.4 (0.1-79.4) umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <3.6 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 29.9 (0.1-78.9) umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <5 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Not Specified | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | <4 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 8.2 (1.5-30.8) umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 3.7 (1.1-21.6) umol/mmol creatinine | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 1.3 (0.5-2.1) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Normal | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 10-20 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Both | Normal | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| |
| Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.466-188.842 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | cobalamin deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 11.2 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Heart Transplant | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 22.0 (4.3-37.0) uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Cobalamin deficiency | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.480 +/- 0.062 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Alzheimer's disease | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 10-15.4 uM | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 1.3-4.1 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Methylmalonic aciduria mitochondrial encephelopathy Leigh-like | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 5-100 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Methylmalonic aciduria, cblA type | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 5-100 uM | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Methylmalonic aciduria, cblB type | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 0.8-33 uM | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Mitochondrial encephalomyopaththy with elevanted methylmalonic acid, SUCLA2 | | details | | Blood | Detected and Quantified | 2.8 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Female | Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 13 uM | Adolescent (13-18 years old) | Female | Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency | | details | | Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) | Detected and Quantified | 0.30 +/- 0.12 uM | Elderly (>65 years old) | Not Specified | Alzheimer's disease | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 29.200-104.500 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 10.435 +/- 7.593 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Eosinophilic esophagitis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 16.0 (1.5-30.8) umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Cobalamin malabsorption | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 275.0 (50.0-500.0) umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Cobalamin malabsorption | | details | | Urine | Detected but not Quantified | Not Quantified | Adult (>18 years old) | Both | Bladder cancer | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Propionic acidemia | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 0.05 umol/mmol creatinine | Adult (>18 years old) | Not Specified | Propionic acidemia | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 3.83 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Male | Fumarase deficiency | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 33 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Male | Malonyl-Coa decarboxylase deficiency | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 126-904 umol/mmol creatinine | Newborn (0-30 days old) | Female | Transcobalamin II deficiency | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 97.67 +/- 89.432 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Eosinophilic esophagitis | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 17.779 +/- 21.646 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1 - 13 years old) | Not Specified | Gastroesophageal reflux disease | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 16-80 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Methylmalonic aciduria mitochondrial encephelopathy Leigh-like | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 10-100 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Methylmalonic aciduria, cblA type | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 10-100 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Both | Methylmalonic aciduria, cblB type | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 51-212 umol/mmol creatinine | Children (1-13 years old) | Both | Mitochondrial encephalomyopaththy with elevanted methylmalonic acid, SUCLA2 | | details | | Urine | Detected and Quantified | 200 umol/mmol creatinine | Infant (0-1 year old) | Female | Cobalamin F disease (cblF) | | details |
| Show more...
|---|
| Associated Disorders and Diseases |
|---|
| Disease References | | Vitamin B12 deficiency |
|---|
- Hoffmann GF, Meier-Augenstein W, Stockler S, Surtees R, Rating D, Nyhan WL: Physiology and pathophysiology of organic acids in cerebrospinal fluid. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1993;16(4):648-69. [PubMed:8412012 ]
- Stabler SP, Marcell PD, Podell ER, Allen RH, Lindenbaum J: Assay of methylmalonic acid in the serum of patients with cobalamin deficiency using capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1606-12. [PubMed:3700655 ]
| | Malonyl-Coa decarboxylase deficiency |
|---|
- Polinati PP, Valanne L, Tyni T: Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase deficiency: long-term follow-up of a patient new clinical features and novel mutations. Brain Dev. 2015 Jan;37(1):107-13. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Mar 7. [PubMed:24613099 ]
- Haan EA, Scholem RD, Croll HB, Brown GK: Malonyl coenzyme A decarboxylase deficiency. Clinical and biochemical findings in a second child with a more severe enzyme defect. Eur J Pediatr. 1986 Apr;144(6):567-70. [PubMed:3709568 ]
| | Methylmalonic aciduria mitochondrial encephelopathy Leigh-like |
|---|
- Carrozzo R, Dionisi-Vici C, Steuerwald U, Lucioli S, Deodato F, Di Giandomenico S, Bertini E, Franke B, Kluijtmans LA, Meschini MC, Rizzo C, Piemonte F, Rodenburg R, Santer R, Santorelli FM, van Rooij A, Vermunt-de Koning D, Morava E, Wevers RA: SUCLA2 mutations are associated with mild methylmalonic aciduria, Leigh-like encephalomyopathy, dystonia and deafness. Brain. 2007 Mar;130(Pt 3):862-74. Epub 2007 Feb 14. [PubMed:17301081 ]
| | Methylmalonic aciduria, cblA type |
|---|
- Keyfi F, Talebi S, Varasteh AR: Methylmalonic Acidemia Diagnosis by Laboratory Methods. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Oct;5(1):1-14. [PubMed:28070528 ]
| | Methylmalonic aciduria, cblB type |
|---|
- Keyfi F, Talebi S, Varasteh AR: Methylmalonic Acidemia Diagnosis by Laboratory Methods. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Oct;5(1):1-14. [PubMed:28070528 ]
| | Mitochondrial encephalomyopaththy with elevanted methylmalonic acid, SUCLA2 |
|---|
- Ostergaard E, Hansen FJ, Sorensen N, Duno M, Vissing J, Larsen PL, Faeroe O, Thorgrimsson S, Wibrand F, Christensen E, Schwartz M: Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy with elevated methylmalonic acid is caused by SUCLA2 mutations. Brain. 2007 Mar;130(Pt 3):853-61. Epub 2007 Feb 7. [PubMed:17287286 ]
| | Alzheimer's disease |
|---|
- Serot JM, Barbe F, Arning E, Bottiglieri T, Franck P, Montagne P, Nicolas JP: Homocysteine and methylmalonic acid concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid: relation with age and Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005 Nov;76(11):1585-7. [PubMed:16227558 ]
- Kristensen MO, Gulmann NC, Christensen JE, Ostergaard K, Rasmussen K: Serum cobalamin and methylmalonic acid in Alzheimer dementia. Acta Neurol Scand. 1993 Jun;87(6):475-81. [PubMed:8356878 ]
| | Cobalamin malabsorption |
|---|
- G.Frauendienst-Egger, Friedrich K. Trefz (2017). MetaGene: Metabolic & Genetic Information Center (MIC: http://www.metagene.de). METAGENE consortium.
| | Eosinophilic esophagitis |
|---|
- Slae, M., Huynh, H., Wishart, D.S. (2014). Analysis of 30 normal pediatric urine samples via NMR spectroscopy (unpublished work). NA.
| | Propionic acidemia |
|---|
- Riemersma M, Hazebroek MR, Helderman-van den Enden ATJM, Salomons GS, Ferdinandusse S, Brouwers MCGJ, van der Ploeg L, Heymans S, Glatz JFC, van den Wijngaard A, Krapels IPC, Bierau J, Brunner HG: Propionic acidemia as a cause of adult-onset dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur J Hum Genet. 2017 Nov;25(11):1195-1201. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2017.127. Epub 2017 Aug 30. [PubMed:28853722 ]
| | Fumarase deficiency |
|---|
- Bastug O, Kardas F, Ozturk MA, Halis H, Memur S, Korkmaz L, Tag Z, Gunes T: A rare cause of opistotonus; fumaric aciduria: The first case presentation in Turkey. Turk Pediatri Ars. 2014 Mar 1;49(1):74-6. doi: 10.5152/tpa.2014.442. eCollection 2014 Mar. [PubMed:26078636 ]
| | Transcobalamin II deficiency |
|---|
- Bibi H, Gelman-Kohan Z, Baumgartner ER, Rosenblatt DS: Transcobalamin II deficiency with methylmalonic aciduria in three sisters. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1999 Oct;22(7):765-72. [PubMed:10518276 ]
| | Cobalamin F disease (cblF) |
|---|
- Alfadhel M, Lillquist YP, Davis C, Junker AK, Stockler-Ipsiroglu S: Eighteen-year follow-up of a patient with cobalamin F disease (cblF): report and review. Am J Med Genet A. 2011 Oct;155A(10):2571-7. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.34220. Epub 2011 Sep 9. [PubMed:21910240 ]
| | Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria |
|---|
- Sloan JL, Johnston JJ, Manoli I, Chandler RJ, Krause C, Carrillo-Carrasco N, Chandrasekaran SD, Sysol JR, O'Brien K, Hauser NS, Sapp JC, Dorward HM, Huizing M, Barshop BA, Berry SA, James PM, Champaigne NL, de Lonlay P, Valayannopoulos V, Geschwind MD, Gavrilov DK, Nyhan WL, Biesecker LG, Venditti CP: Exome sequencing identifies ACSF3 as a cause of combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria. Nat Genet. 2011 Aug 14;43(9):883-6. doi: 10.1038/ng.908. [PubMed:21841779 ]
|
|
|---|
| Associated OMIM IDs | - 248360 (Malonyl-Coa decarboxylase deficiency)
- 251100 (Methylmalonic aciduria, cblA type)
- 251110 (Methylmalonic aciduria, cblB type)
- 612073 (Mitochondrial encephalomyopaththy with elevanted methylmalonic acid, SUCLA2)
- 104300 (Alzheimer's disease)
- 610247 (Eosinophilic esophagitis)
- 606054 (Propionic acidemia)
- 606812 (Fumarase deficiency)
- 275350 (Transcobalamin II deficiency)
- 277380 (Cobalamin F disease (cblF))
- 614265 (Combined malonic and methylmalonic aciduria)
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB04183 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB021905 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 473 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C02170 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | CPD-546 |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Methylmalonic_acid |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 3712 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 487 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 30860 |
|---|
| Food Biomarker Ontology | Not Available |
|---|
| VMH ID | HC00900 |
|---|
| MarkerDB ID | MDB00000097 |
|---|
| Good Scents ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Edamura, Koji; Arai, Takeshi. Malonic and methylmalonic acids from b-hydroxypropionic acids. Jpn. Kokai Tokkyo Koho (1979), 5 pp. |
|---|
| Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Guneral F, Bachmann C: Age-related reference values for urinary organic acids in a healthy Turkish pediatric population. Clin Chem. 1994 Jun;40(6):862-6. [PubMed:8087979 ]
- Haurani FI, Hall CA, Rubin R: Megaloblastic anemia as a result of an abnormal transcobalamin II (Cardeza). J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1253-9. [PubMed:500809 ]
- Bennett MJ, Ragni MC, Hood I, Hale DE: Comparison of post-mortem urinary and vitreous humour organic acids. Ann Clin Biochem. 1992 Sep;29 ( Pt 5):541-5. [PubMed:1444166 ]
- van Asselt DZ, Karlietis MH, Poels PJ, de Jong JG, Wevers RA, Hoefnagels WH: Cerebrospinal fluid methylmalonic acid concentrations in neurological patients with low and normal serum cobalamin concentrations. Acta Neurol Scand. 1998 Jun;97(6):413-6. [PubMed:9669477 ]
- Magera MJ, Helgeson JK, Matern D, Rinaldo P: Methylmalonic acid measured in plasma and urine by stable-isotope dilution and electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2000 Nov;46(11):1804-10. [PubMed:11067816 ]
- Nakamura E, Rosenberg LE, Tanaka K: Microdetermination of methylmalonic acid and other short chain dicarboxylic acids by gas chromatography: use in prenatal diagnosis of methylmalonic acidemia and in studies of isovaleric acidemia. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Apr 15;68(2):127-40. [PubMed:1261058 ]
- Jakobs C, Sweetman L, Nyhan WL: Hydroxy acid metabolites of branched-chain amino acids in amniotic fluid. Clin Chim Acta. 1984 Jul 16;140(2):157-66. [PubMed:6467607 ]
- Coude MM, Charpentier C, Bonnefont JP, Cheron G, Kamoun P: Organic acids in aqueous humour and plasma: post mortem study in infants and diagnosis of enzymopathies. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1991;14(5):668-73. [PubMed:1779612 ]
- Aleszczyk J: [Connection between changing the vitamin and immune status and the character of the throat microflora in patients with chronic tonsillitis]. Otolaryngol Pol. 2003;57(2):221-4. [PubMed:12894427 ]
- Nagarajan S, Enns GM, Millan MT, Winter S, Sarwal MM: Management of methylmalonic acidaemia by combined liver-kidney transplantation. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2005;28(4):517-24. [PubMed:15902554 ]
- Stabler SP, Marcell PD, Podell ER, Allen RH, Lindenbaum J: Assay of methylmalonic acid in the serum of patients with cobalamin deficiency using capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1606-12. [PubMed:3700655 ]
- Jellum E, Stokke O, Eldjarn L: Combined use of gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and computer in diagnosis and studies of metabolic disorders. Clin Chem. 1972 Aug;18(8):800-9. [PubMed:4557757 ]
- Leupold D: [Methylmalonic aciduria. Classification, diagnosis and therapy (author's transl)]. Klin Wochenschr. 1977 Jan 15;55(2):57-63. [PubMed:319293 ]
- Vrethem M, Mattsson E, Hebelka H, Leerbeck K, Osterberg A, Landtblom AM, Balla B, Nilsson H, Hultgren M, Brattstrom L, Kagedal B: Increased plasma homocysteine levels without signs of vitamin B12 deficiency in patients with multiple sclerosis assessed by blood and cerebrospinal fluid homocysteine and methylmalonic acid. Mult Scler. 2003 Jun;9(3):239-45. [PubMed:12814169 ]
- Frenkel EP, Kitchens RL: Applicability of an enzymatic quantitation of methylmalonic, propionic, and acetic acids in normal and megaloblastic states. Blood. 1977 Jan;49(1):125-37. [PubMed:830370 ]
- Elshenawy S, Pinney SE, Stuart T, Doulias PT, Zura G, Parry S, Elovitz MA, Bennett MJ, Bansal A, Strauss JF 3rd, Ischiropoulos H, Simmons RA: The Metabolomic Signature of the Placenta in Spontaneous Preterm Birth. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 4;21(3). pii: ijms21031043. doi: 10.3390/ijms21031043. [PubMed:32033212 ]
| Show more...
|---|